StorageClass
Harvester uses StorageClasses to describe how Longhorn must provision volumes. Longhorn StorageClasses can map to replica policies, node schedule policies, or disk schedule policies created by the cluster administrators. This concept is referred to as profiles in other storage systems.
The default StorageClass harvester-longhorn has a replica count value of 3 for high availability. If you use harvester-longhorn in a single-node cluster, Longhorn is unable to create the default number of replicas, and volumes are marked as Degraded on the Harvester UI.
To avoid this issue, you can perform either of the following actions:
-
Change the replica count of
harvester-longhornto1using a Harvester configuration file. -
Create a new StorageClass with the Number of Replicas parameter set to
1. Once created, locate the new StorageClass in the list and then select ⋮ > Set as Default.
For information about support for volume provisioning using external container storage interface (CSI) drivers, see Third-Party Storage Support.
Creating a StorageClass
- UI
- API
- Terraform
After a StorageClass is created, the fields in the Parameters section and most of the other options become immutable.
-
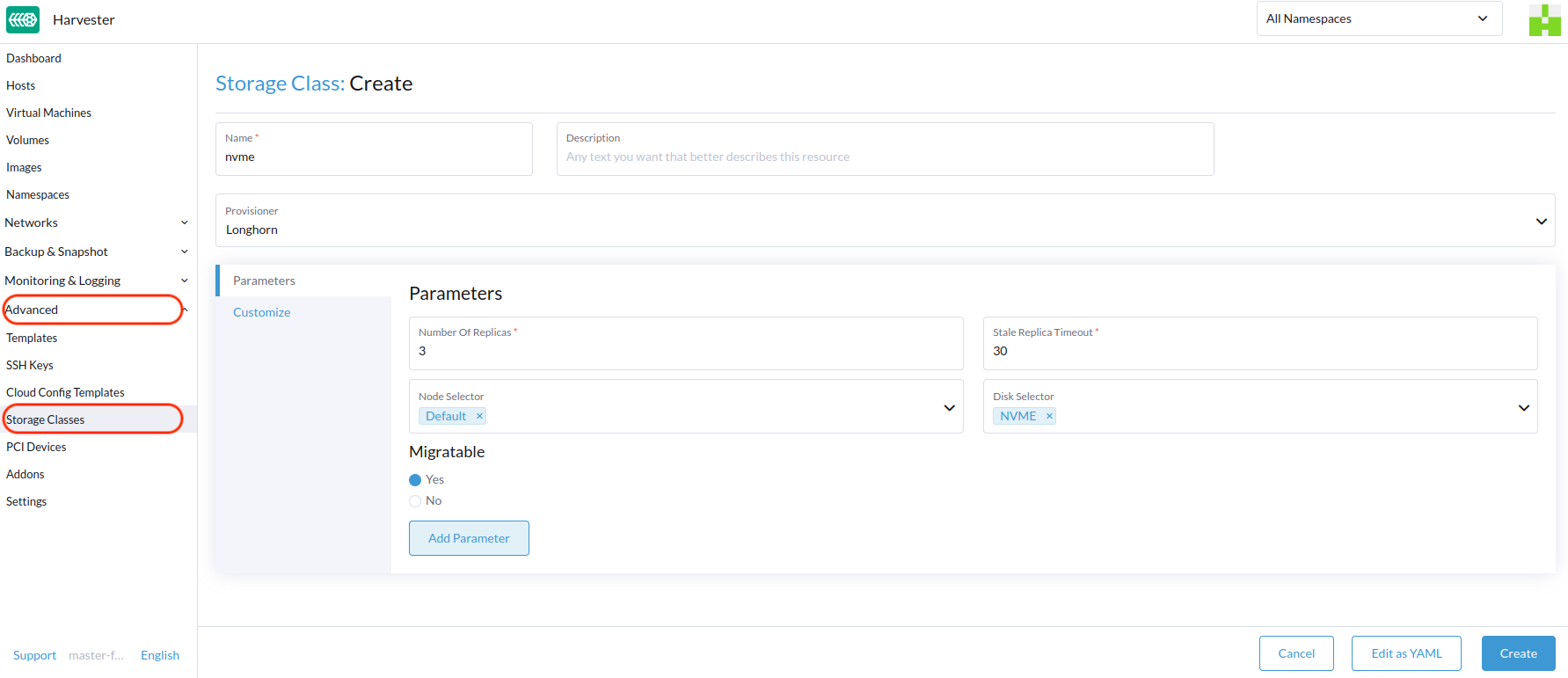
On the Harvester UI, go to Advanced > StorageClasses.
-
In the general information section, configure the following:
- Name: Name of the StorageClass.
- Description (optional): Description of the StorageClass.
- Provisioner: Provisioner that determines the volume plugin to be used for provisioning volumes.
-
On the Parameters tab, configure the following:
- Number of Replicas: Number of replicas created for each Longhorn volume. The default value is
3. - Stale Replica Timeout: Number of minutes Longhorn waits before cleaning up a replica with the status
ERROR. The default value is30. - Node Selector (optional): Node tags to be matched during volume scheduling. You can add node tags on the host configuration screen (Host -> Edit Config).
- Disk Selector (optional): Disk tags to be matched during volume scheduling. You can add disk tags on the host configuration screen (Host -> Edit Config).
- Migratable: Setting that enables Live Migration for volumes created using the StorageClass. The default value is
Yes.
cautionIf a StorageClass with a replica count of
1is used to create a volume that is attached to a virtual machine, that virtual machine is considered non-migratable. - Number of Replicas: Number of replicas created for each Longhorn volume. The default value is
-
On the Customize tab, configure the following:
-
Reclaim Policy: Reclaim policy that applies to volumes created using the StorageClass. The default value is
Delete.Delete: Deletes volumes and the underlying devices when the volume claim is deleted.Retain: Retains the volume for manual cleanup.
-
Allow Volume Expansion: Setting that allows volume expansion, which involves resizing of the block device and expansion of the filesystem. When the setting is enabled, you can increase the volume size by editing the corresponding PVC object. The default value is
Enabled.noteYou can only use the volume expansion feature to increase the volume size.
-
Volume Binding Mode: Setting that controls when volume binding and dynamic provisioning occur. The default value is
Immediate.- Immediate: Binds and provisions a volume once the PVC is created.
- WaitForFirstConsumer: Binds and provisions a volume once a virtual machine using the PVC is created.
-
-
Click Create.
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
annotations:
storageclass.beta.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: 'true'
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: 'true'
name: single-replica
parameters:
migratable: 'false'
numberOfReplicas: '1'
staleReplicaTimeout: '30'
provisioner: driver.longhorn.io
reclaimPolicy: Delete
volumeBindingMode: Immediate
allowVolumeExpansion: true
resource "harvester_storageclass" "single-replica" {
name = "single-replica"
is_default = "true"
allow_volume_expansion = "true"
volume_binding_mode = "immediate"
reclaim_policy = "delete"
parameters = {
"migratable" = "false"
"numberOfReplicas" = "1"
"staleReplicaTimeout" = "30"
}
}
Data Locality Settings
You can use the dataLocality parameter when at least one replica of a Longhorn volume must be scheduled on the same node as the pod that uses the volume (whenever possible).
Harvester officially supports data locality as of v1.3.0. This applies even to volumes created from images. To configure data locality, create a new StorageClass on the Harvester UI (Storage Classess > Create > Parameters) and then add the following parameter:
- Key:
dataLocality - Value:
disabledorbest-effort
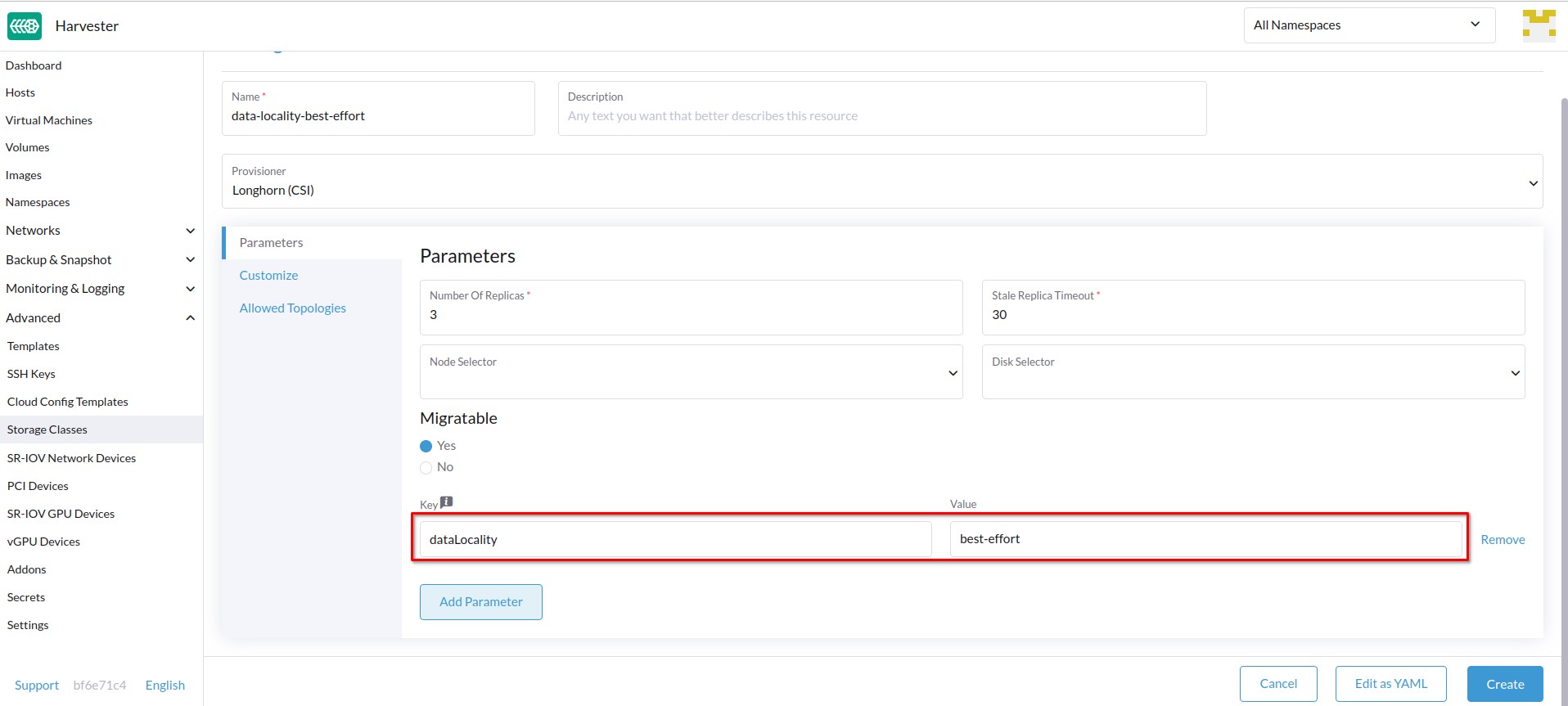
Data Locality Options
Harvester currently supports the following options:
-
disabled: When applied, Longhorn may or may not schedule a replica on the same node as the pod that uses the volume. This is the default option. -
best-effort: When applied, Longhorn always attempts to schedule a replica on the same node as the pod that uses the volume. Longhorn does not stop the volume even when a local replica is unavailable because of an environmental limitation (for example, insufficient disk space or incompatible disk tags).
Longhorn provides a third option called strict-local, which forces Longhorn to keep only one replica on the same node as the pod that uses the volume. Harvester does not support this option because it can affect certain operations such as VM Live Migration
For more information, see Data Locality in the Longhorn documentation.
Containerized Data Importer (CDI) Settings
Harvester integrates with the Containerized Data Importer (CDI) to handle VM image management for the following StorageClasses:
- Longhorn V2 Data Engine
- LVM
- Third-party storage
You can use the Harvester UI or CDI annotations to override the default settings of a storage class CDI attributes.
The Harvester UI currently does not support the use of CDI with third-party storage. Instead, apply the Harvester CDI annotations directly to the third-party storage class.
To enable editing of CDI settings for day-2 operations, Harvester provides StorageClass attributes that automatically update the underlying CDI settings.
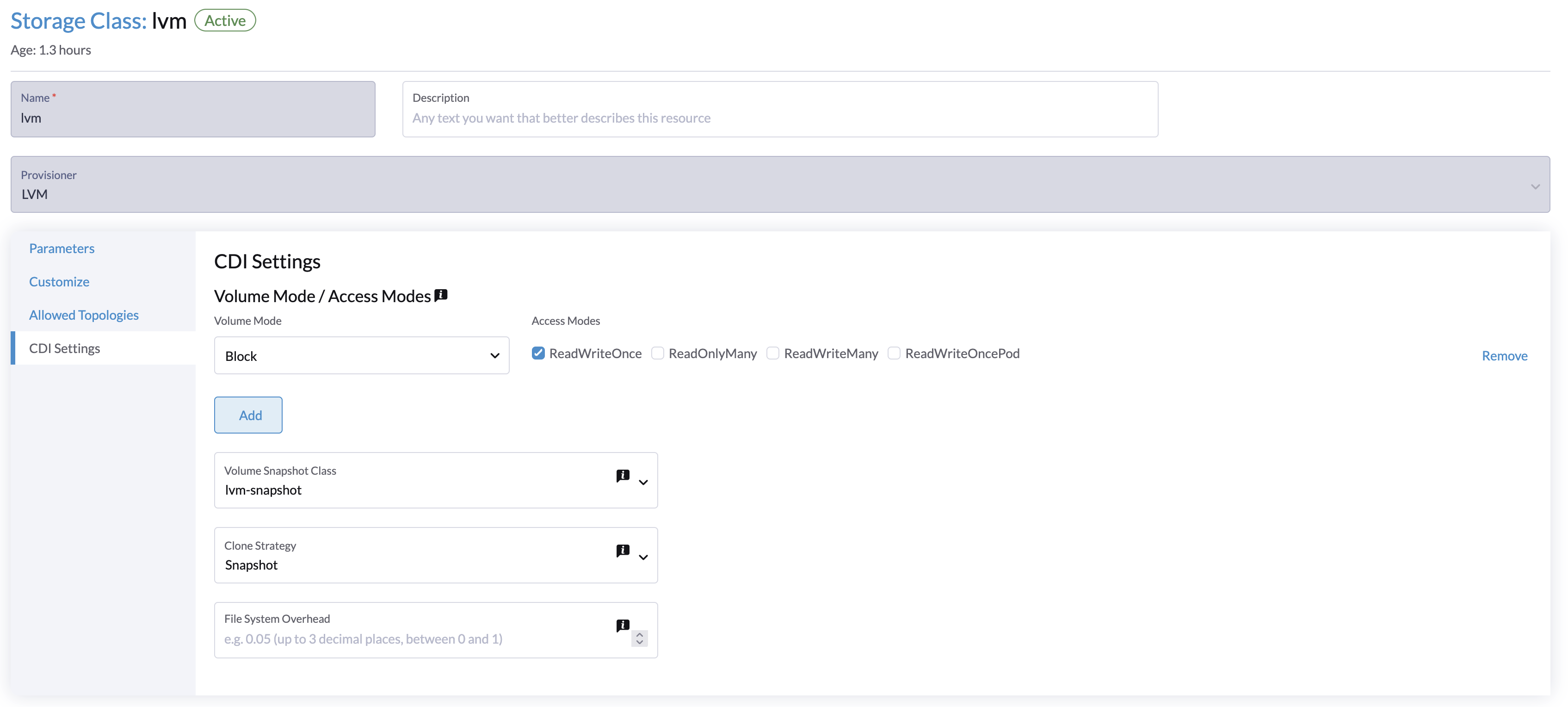
Each field on the CDI Settings screen corresponds to an annotation in the StorageClass.
| UI Field | Annotation | Description | Supported Values | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volume Mode / Access Modes | cdi.harvesterhci.io/storageProfileVolumeModeAccessModes | Default PVC volume mode and access modes | JSON object with volume modes and access modes | '{"Block":["ReadWriteOnce"]}' |
| Volume Snapshot Class | cdi.harvesterhci.io/storageProfileVolumeSnapshotClass | VolumeSnapshotClass name to be used when taking snapshots of virtual machine images under this StorageClass. This setting applies only when you are using the snapshot clone strategy. If you have already configured the volumeSnapshotClassName in the csi-driver-config setting for the corresponding provisioner, that value will be used as the default. | Valid VolumeSnapshotClass name | lvm-snapshot, longhorn-snapshot |
| Clone Strategy | cdi.harvesterhci.io/storageProfileCloneStrategy | Clone strategy to be used for volumes created with VM images that use this StorageClass. | copy: Copies blocks of data over the networksnapshot: Clones the volume by creating a temporary VolumeSnapshot and restoring it to a new PVCcsi-clone: Clones the volume using a CSI clone operation | snapshot |
| File System Overhead | cdi.harvesterhci.io/filesystemOverhead | Percentage of filesystem overhead to be considered when calculating the PVC size. | Decimal value between 0 and 1 with a maximum of 3 digits | 0.05 |
Here is an example of a StorageClass YAML configuration:
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: lvm
annotations:
cdi.harvesterhci.io/storageProfileCloneStrategy: snapshot
cdi.harvesterhci.io/storageProfileVolumeModeAccessModes: '{"Block":["ReadWriteOnce"]}'
cdi.harvesterhci.io/storageProfileVolumeSnapshotClass: lvm-snapshot
cdi.harvesterhci.io/filesystemOverhead: '0.05'
Avoid changing the storage profile or CDI directly. Instead, allow the Harvester controller to synchronize and persist the storage profile configuration through the use of CDI annotations.
The following are the default values for the supported StorageClasses:
-
Longhorn V2 Data Engine
cdi.harvesterhci.io/storageProfileCloneStrategy:"copy"cdi.harvesterhci.io/storageProfileVolumeSnapshotClass:"longhorn-snapshot"
-
LVM
cdi.harvesterhci.io/storageProfileVolumeModeAccessModes:'{"Block":["ReadWriteOnce"]}'cdi.harvesterhci.io/storageProfileCloneStrategy:"snapshot"cdi.harvesterhci.io/storageProfileVolumeSnapshotClass:"lvm-snapshot"
-
Third-party storage: See
storagecapabilities.goin the CDI repository. If the provisioner is not listed, you must specify thecdi.harvesterhci.io/storageProfileVolumeModeAccessModesannotation.
Use Cases
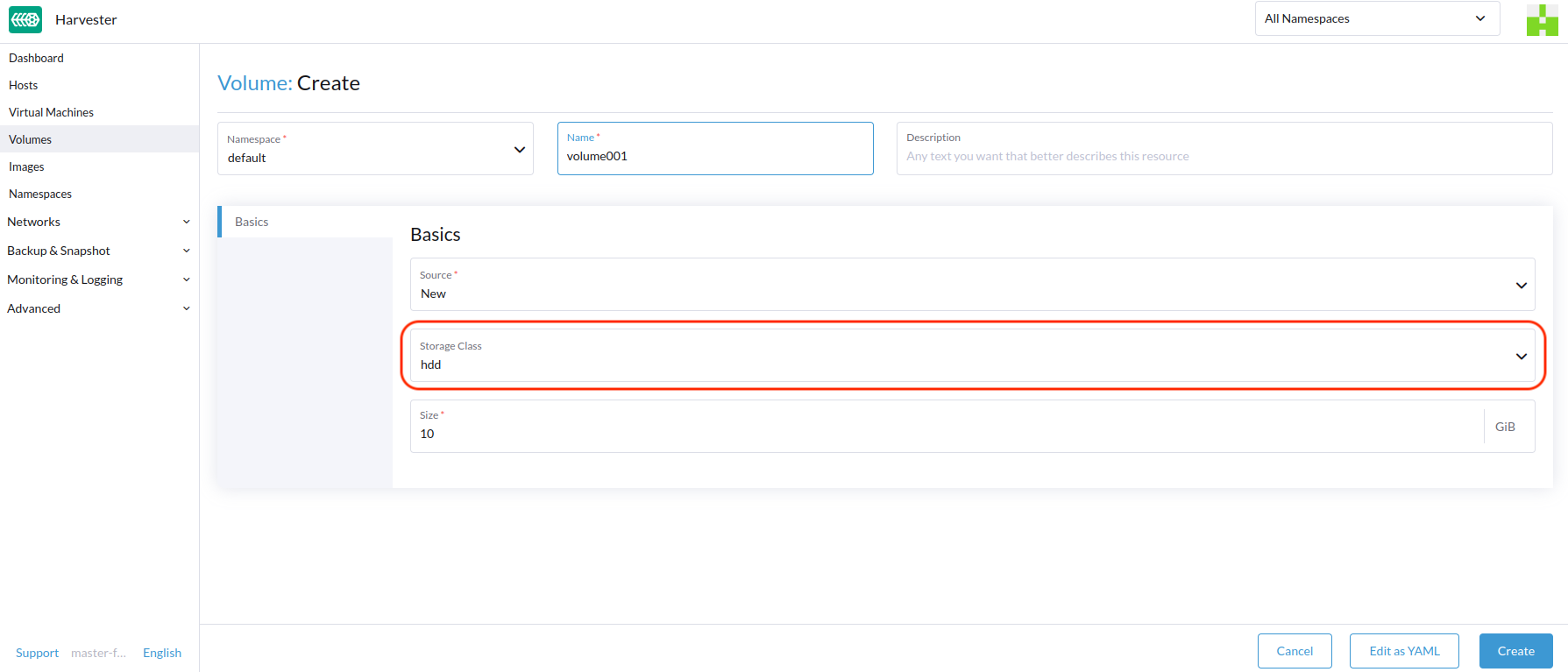
HDD Scenario
With the introduction of StorageClass, users can now use HDDs for tiered or archived cold storage.
HDD is not recommended for guest RKE2 clusters or VMs with good performance disk requirements.
Recommended Practice
First, add your HDD on the Host page and specify the disk tags as needed, such asHDD or ColdStorage. For more information on how to add extra disks and disk tags, see Multi-disk Management for details.
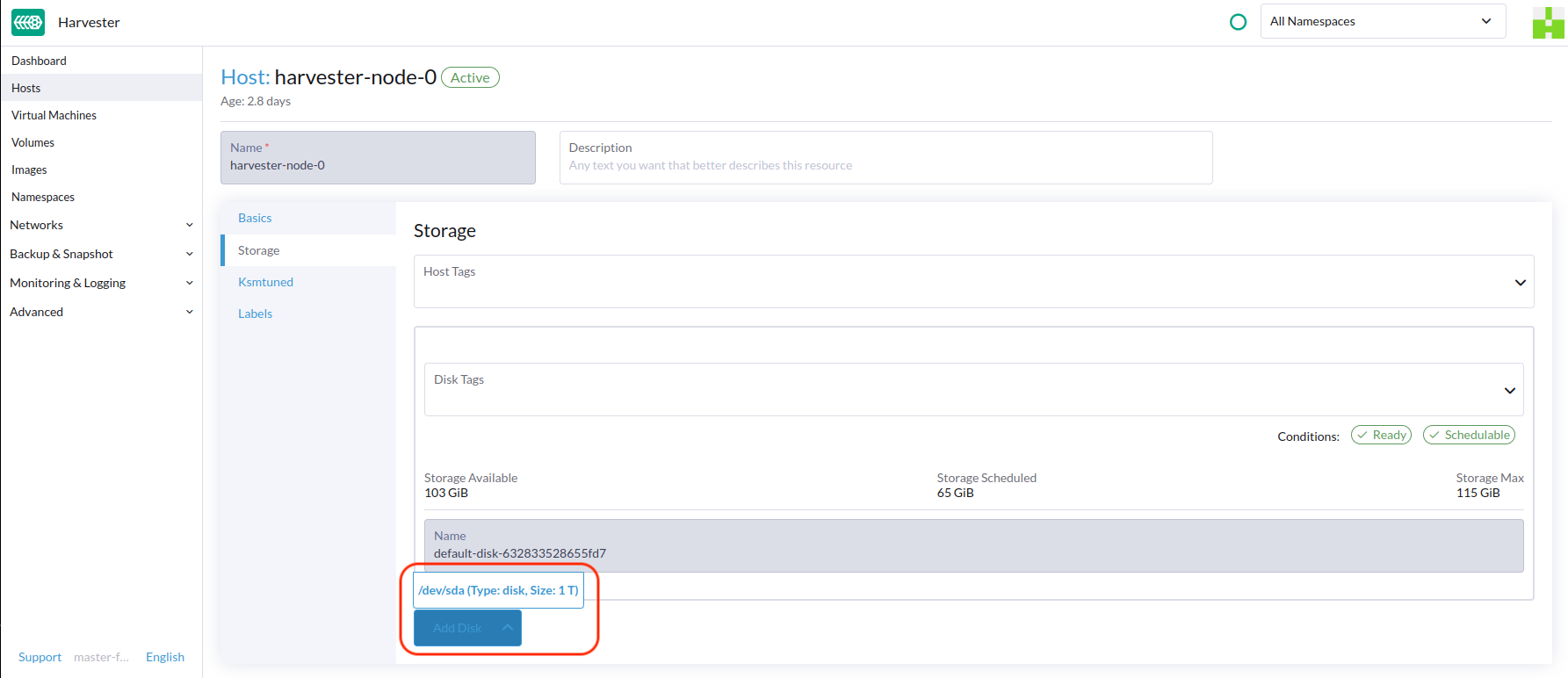
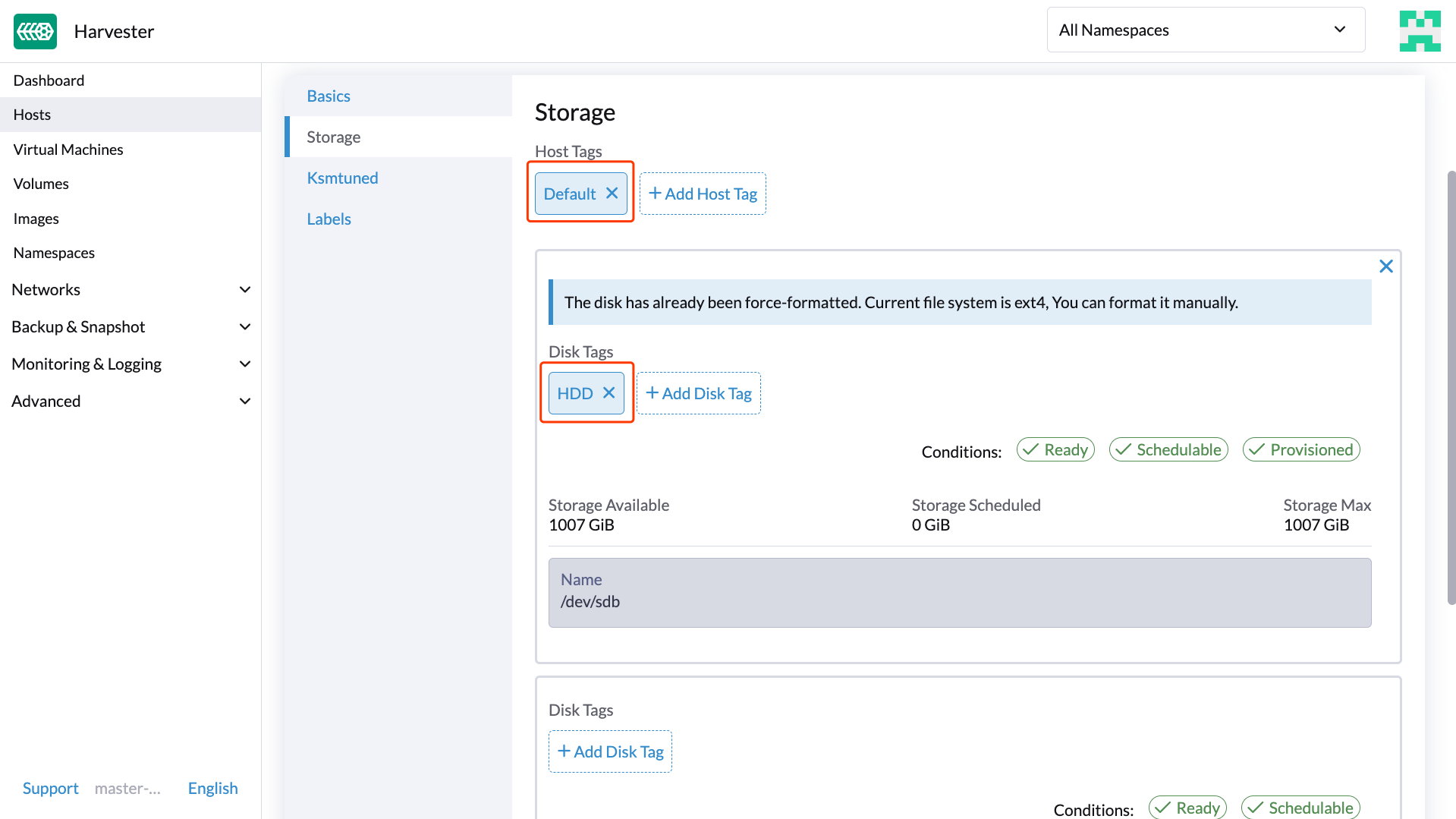
Then, create a new StorageClass for the HDD (use the above disk tags). For hard drives with large capacity but slow performance, the number of replicas can be reduced to improve performance.
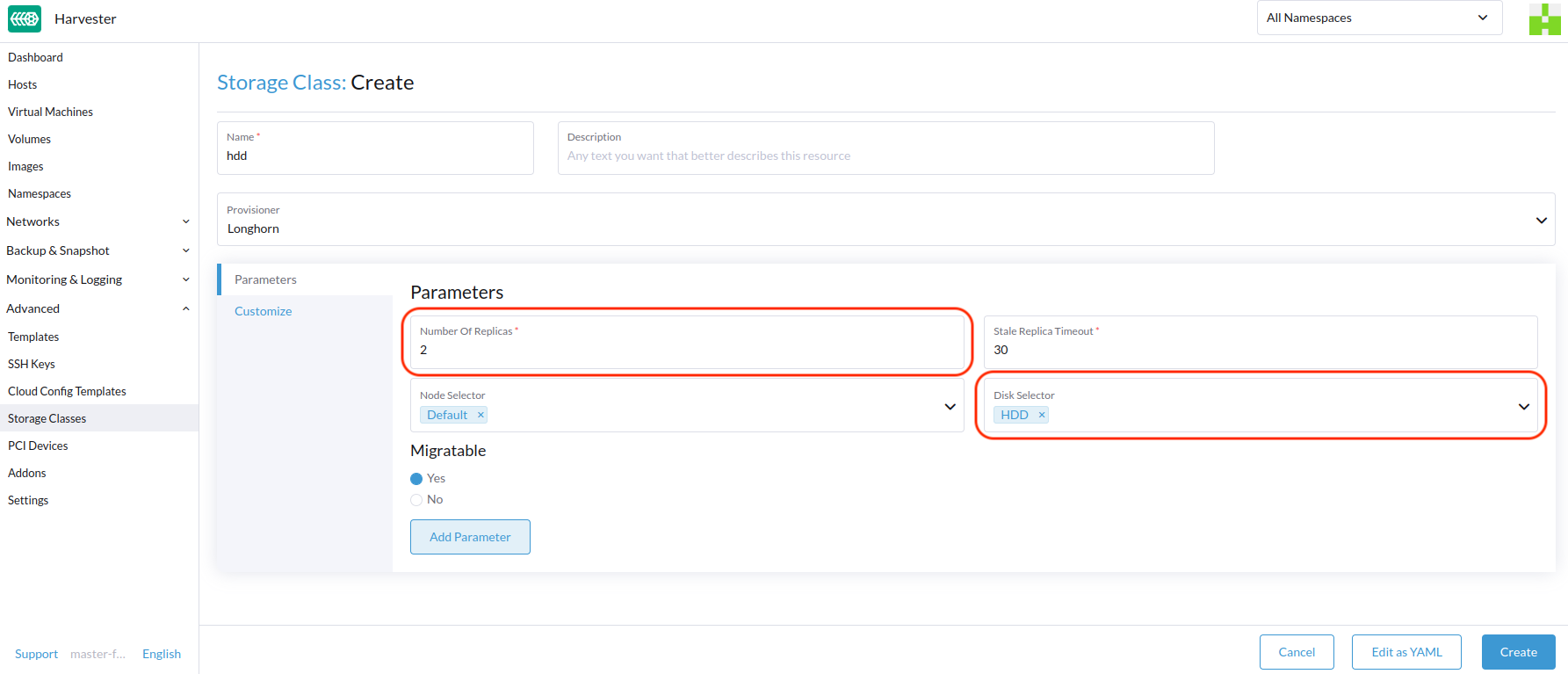
You can now create a volume using the above StorageClass with HDDs mostly for cold storage or archiving purpose.