Air Gapped Environment
This section describes how to use Harvester in an air gapped environment. Some use cases could be where Harvester will be installed offline, behind a firewall, or behind a proxy.
The Harvester ISO image contains all the packages to make it work in an air gapped environment.
Working Behind an HTTP Proxy
In some environments, the connection to external services, from the servers or VMs, requires an HTTP(S) proxy.
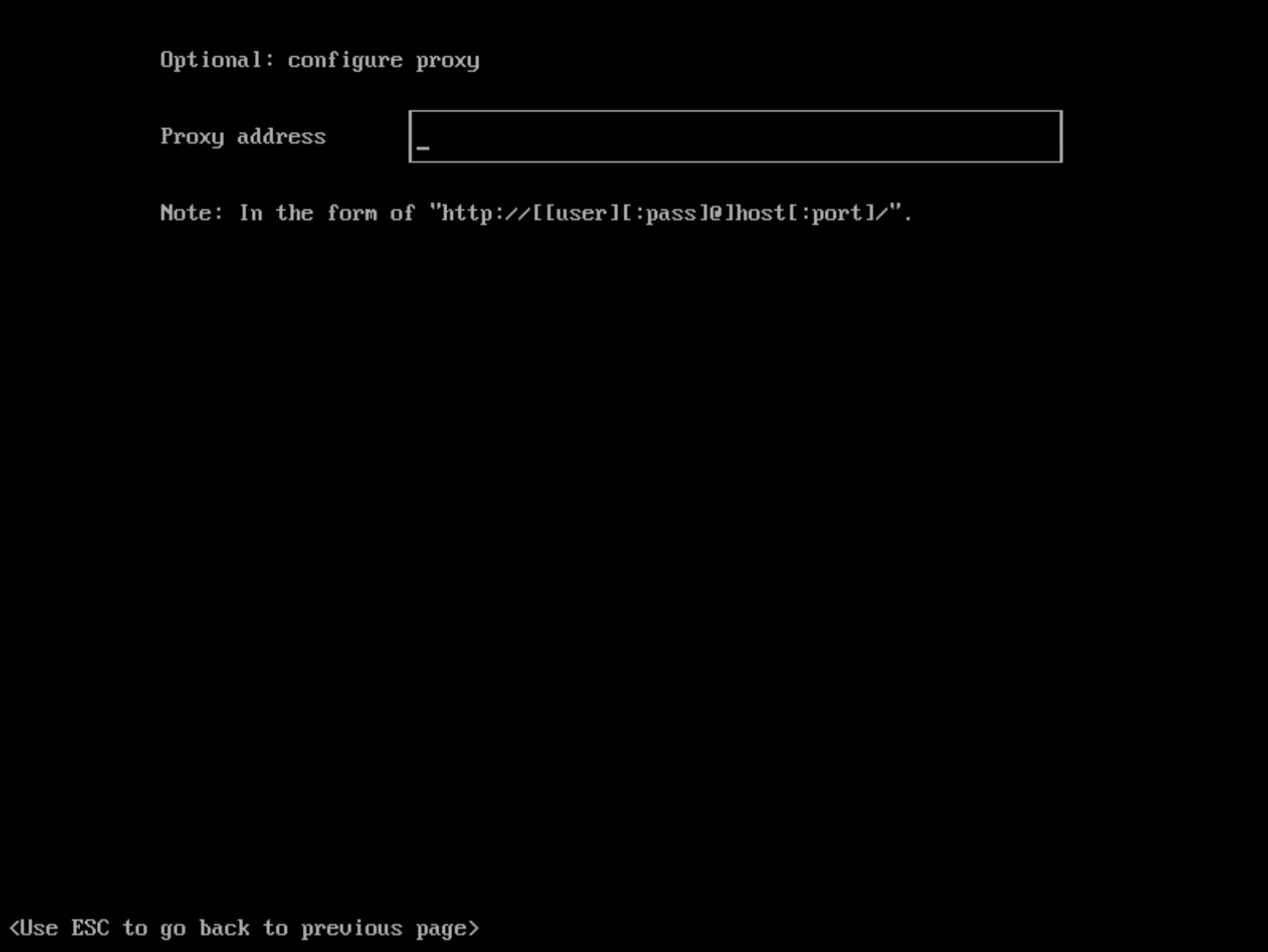
Configure an HTTP Proxy During Installation
You can configure the HTTP(S) proxy during the ISO installation as shown in picture below:
Configure an HTTP Proxy in Harvester Settings
You can configure the HTTP(S) proxy in the settings page of the Harvester dashboard:
- Go to the settings page of the Harvester UI.
- Find the
http-proxysetting, click ⋮ > Edit setting - Enter the value(s) for
http-proxy,https-proxyandno-proxy.
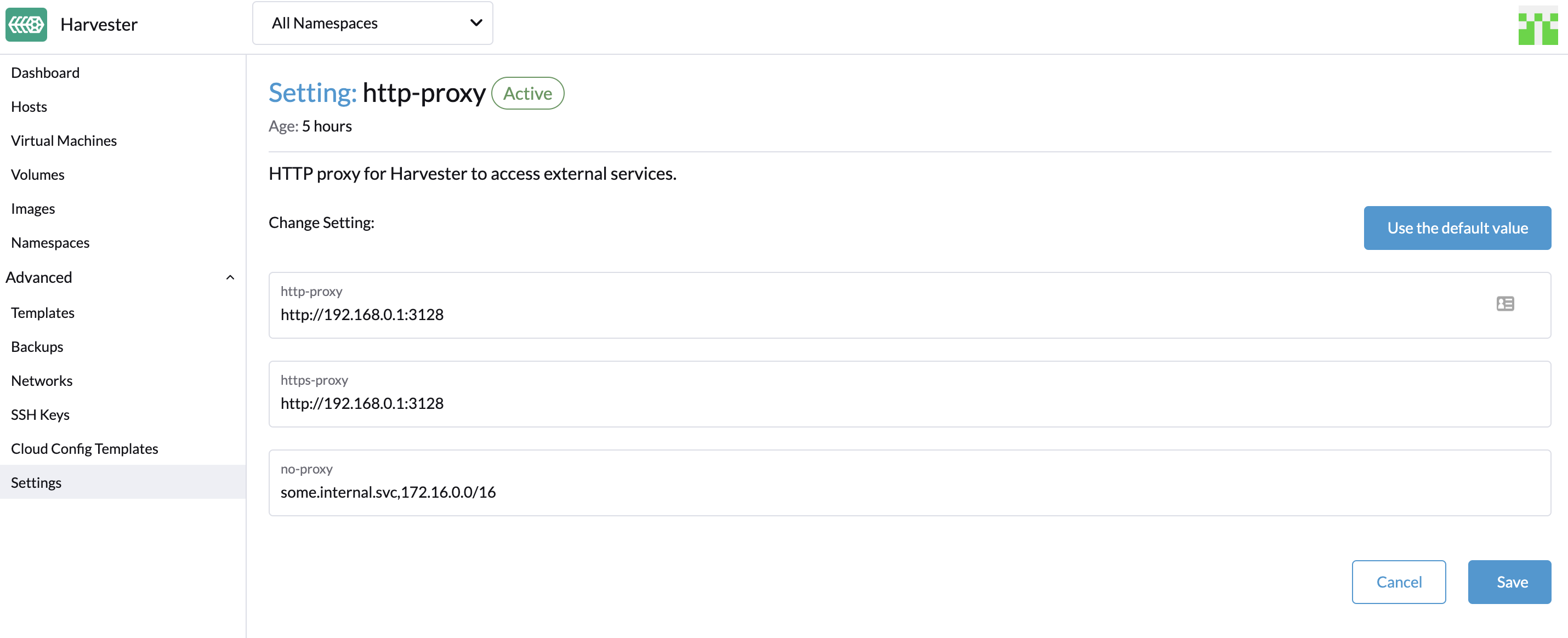
Harvester appends necessary addresses to user configured no-proxy to ensure the internal traffic works.
i.e., localhost,127.0.0.1,0.0.0.0,10.0.0.0/8,longhorn-system,cattle-system,cattle-system.svc,harvester-system,.svc,.cluster.local. harvester-system was added into the list since v1.1.2.
When the nodes in the cluster do not use a proxy to communicate with each other, the CIDR needs to be added to http-proxy.noProxy after the first node is installed successfully. Please refer to fail to deploy a multi-node cluster.
Guest Cluster Images
All necessary images to install and run Harvester are conveniently packaged into the ISO, eliminating the need to pre-load images on bare-metal nodes. A Harvester cluster manages them independently and effectively behind the scenes.
However, it's essential to understand a guest K8s cluster (e.g., RKE2 cluster) created by the Harvester node driver is a distinct entity from a Harvester cluster. A guest cluster operates within VMs and requires pulling images either from the internet or a private registry.
If the Cloud Provider option is configured to Harvester in a guest K8s cluster, it deploys the Harvester cloud provider and Container Storage Interface (CSI) driver.
As a result, we recommend monitoring each RKE2 release in your air gapped environment and pulling the required images into your private registry. Please refer to the Harvester CCM & CSI Driver with RKE2 Releases section on the Harvester support matrix page for the best Harvester cloud provider and CSI driver capability support.
Integrate with External Rancher
Rancher determines the rancher-agent image to be used whenever a Harvester cluster is imported. If the image is not included in the Harvester ISO, it must be pulled from the internet and loaded on each node, or pushed to the Harvester cluster's registry.
# Run the following commands on a computer that can access both the internet and the Harvester cluster.
docker pull rancher/rancher-agent:<version>
docker save rancher/rancher-agent:<version> -o rancher-agent-<version>.tar
# Copy the image TAR file to the air-gapped environment.
scp rancher-agent-<version>.tar rancher@<harvester-node-ip>:/tmp
# Use SSH to connect to the Harvester node, and then load the image.
ssh rancher@<harvester-node-ip>
sudo -i
docker load -i /tmp/rancher-agent-<version>.tar
Harvester UI extension with Rancher Integration
The Harvester UI Extension is required to access the Harvester UI in Rancher v2.10.x and later versions. However, installing the extension over the network is not possible in air-gapped environments, so you must perform the following workaround:
-
Pull the image rancher/ui-plugin-catalog with the newest tag.
-
On the Rancher UI, go to Extensions, and then select ⋮ > Manage Extension Catalogs.
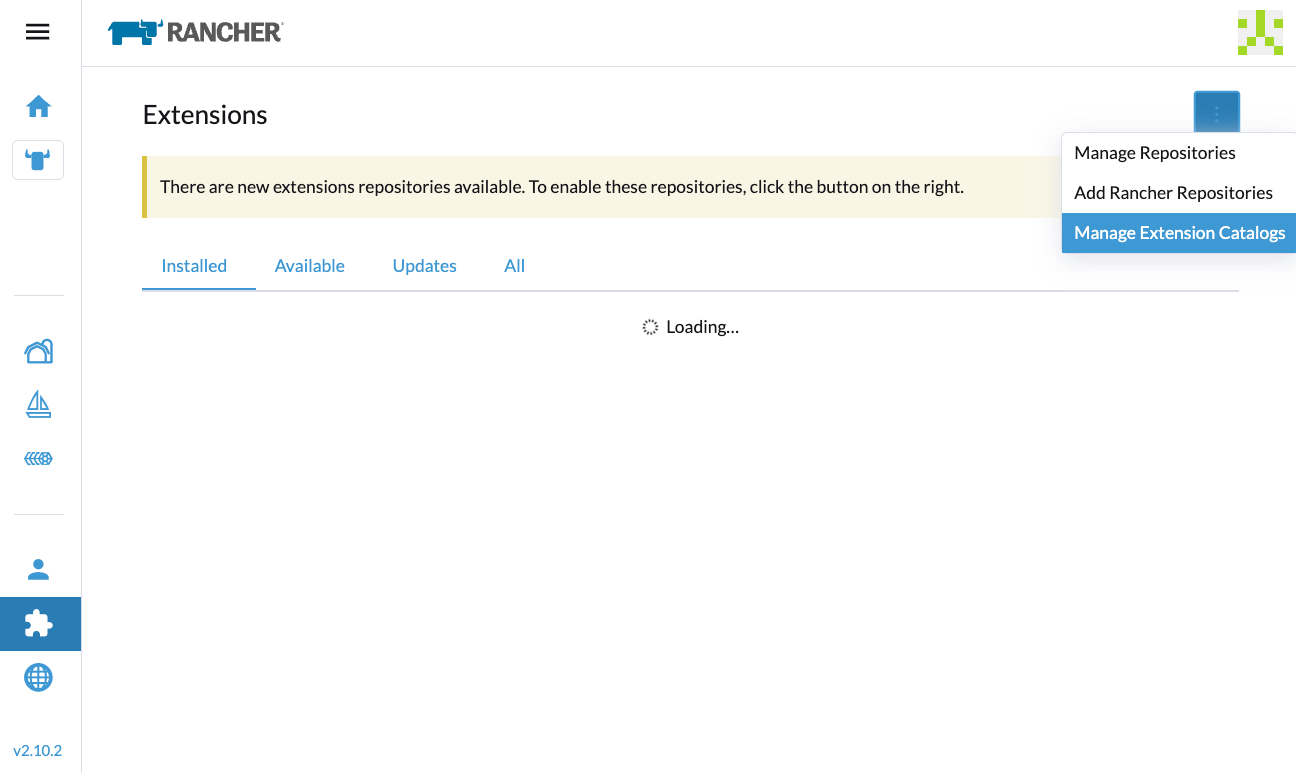
- Specify the required information.
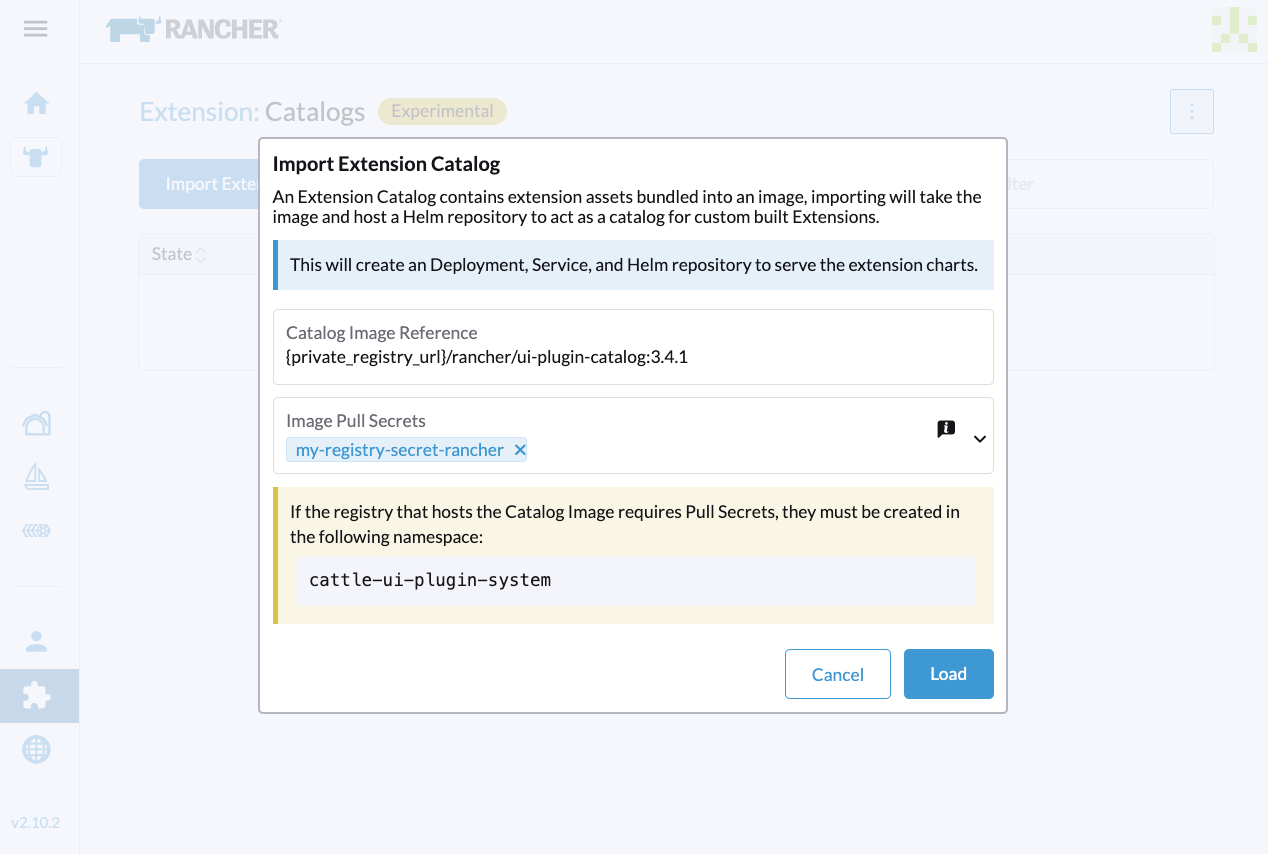
-
Catalog Image Reference: Specify the private registry URL and image repository.
-
Image Pull Secrets: Specify the secret used to access the registry when a username and password are required. You must create that secret in the
cattle-ui-plugin-systemnamespace. Use eitherkubernetes.io/dockercfgorkubernetes.io/dockerconfigjsonas the value oftype. Example:apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: my-registry-secret-rancher
namespace: cattle-ui-plugin-system
type: kubernetes.io/dockerconfigjson
data:
.dockerconfigjson: {base64 encoded data}
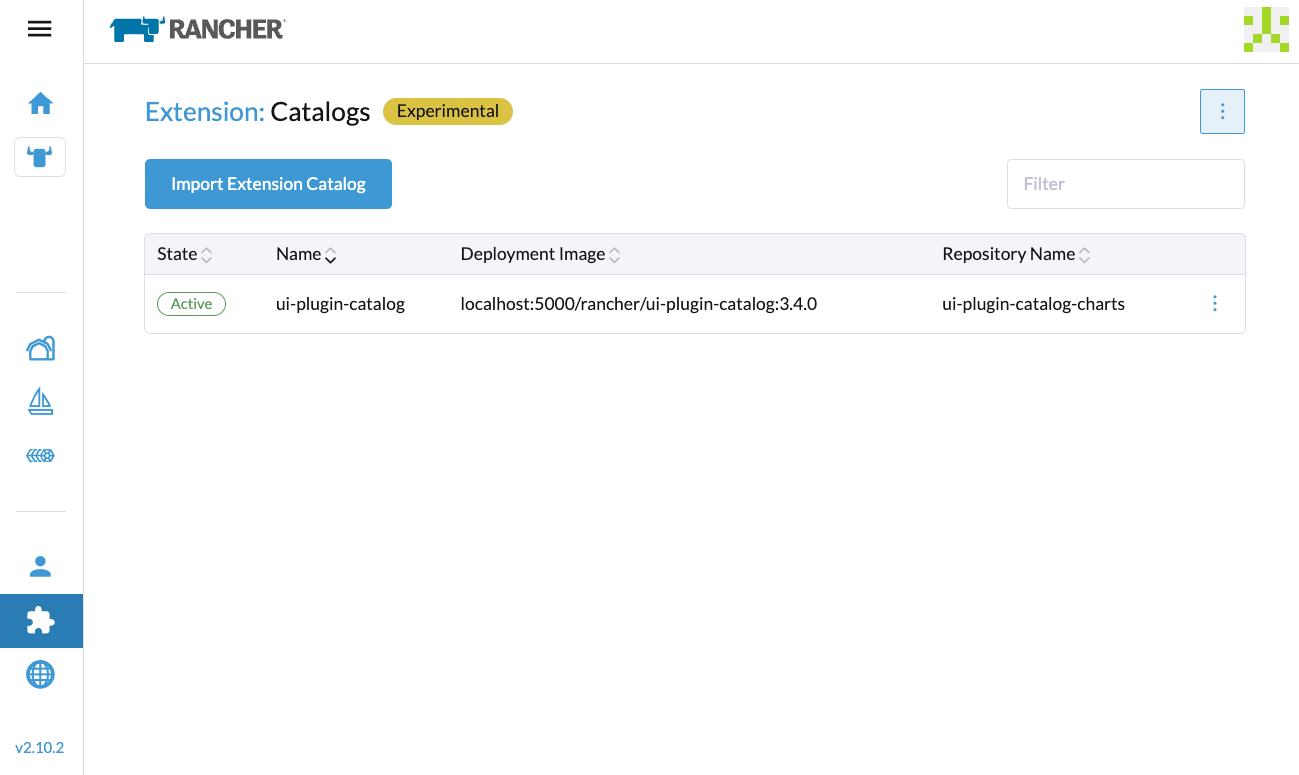
- Click Load, and then allow some time for the extension to be loaded.
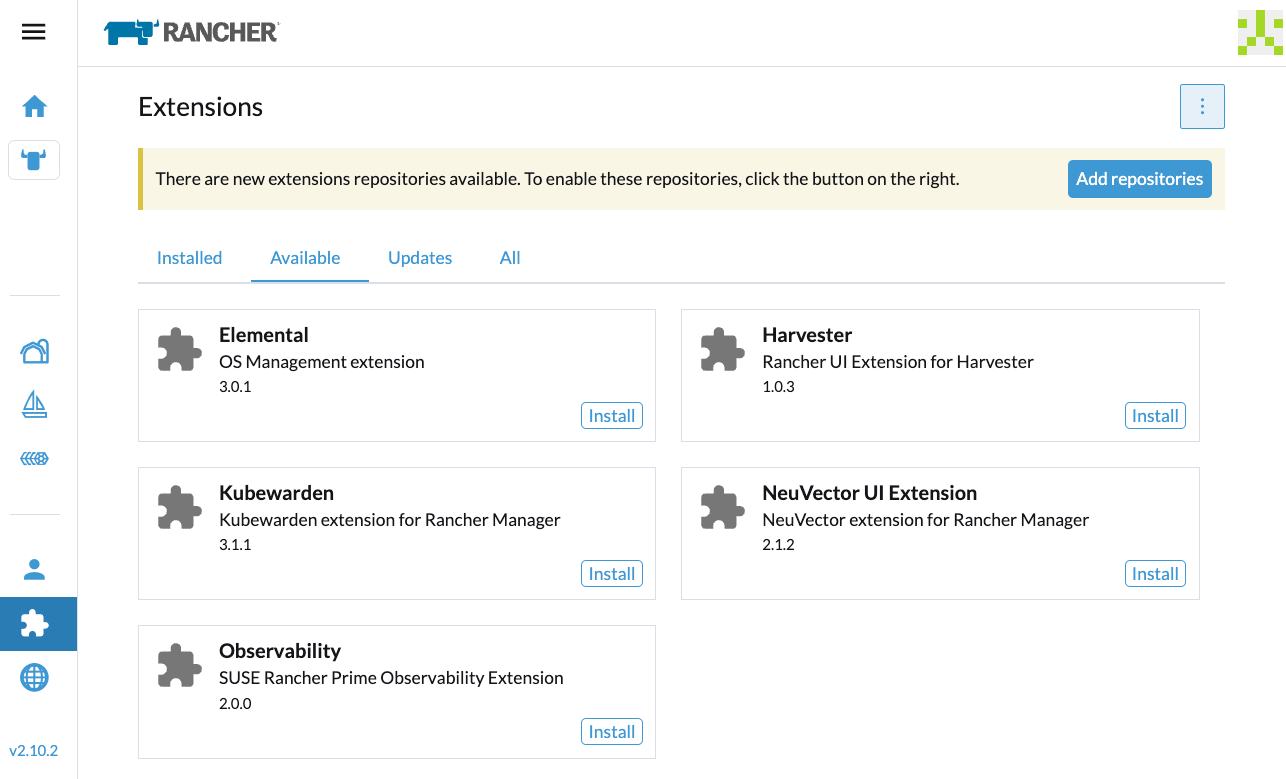
- On the Available tab, locate the extension named Harvester, and then click Install.
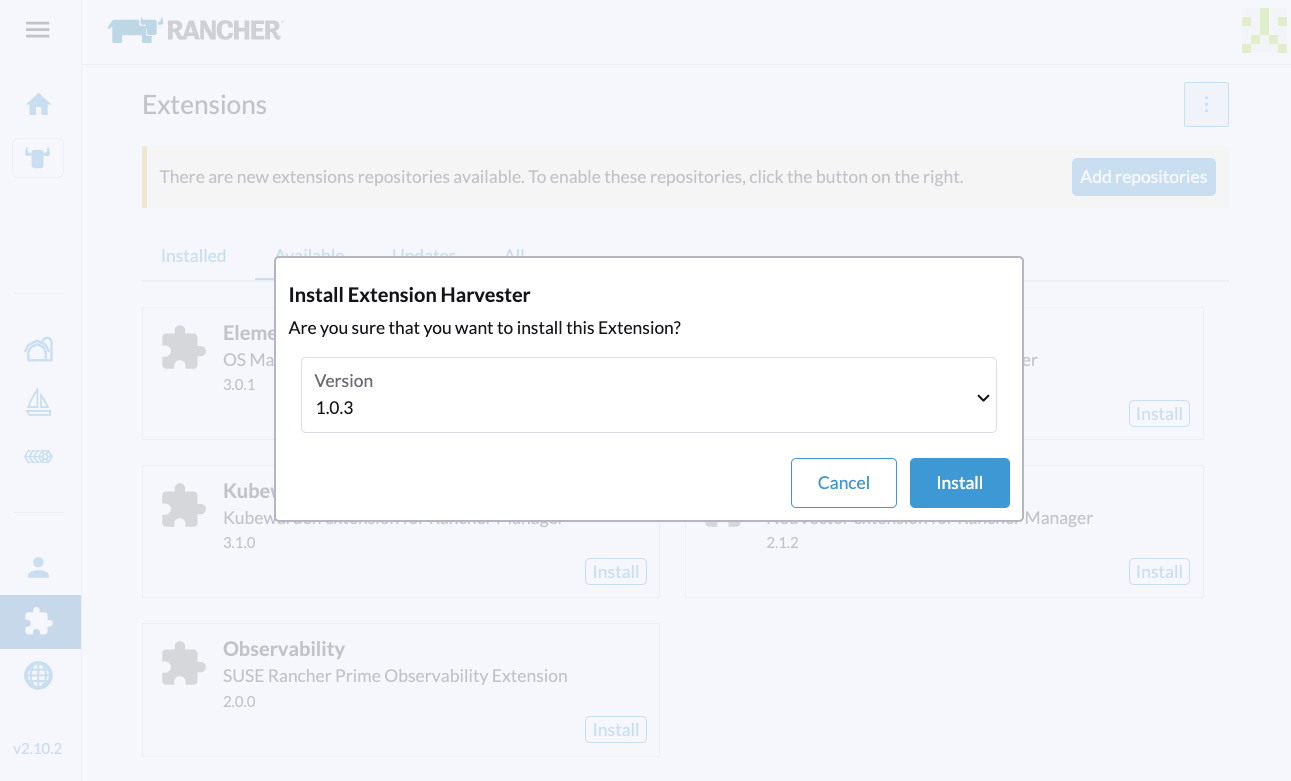
- Select the version that matches the Harvester cluster, and then click Install.
For more information, see the Harvester UI Extension Support Matrix.
- Go to Virtualization Management > Harvester Clusters.
You can now import Harvester clusters and access the Harvester UI.
Time Requirements
A reliable Network Time Protocol (NTP) server is critical for maintaining the correct system time across all nodes in a Kubernetes cluster, especially when running Harvester. Kubernetes relies on etcd, a distributed key-value store, which requires precise time synchronization to ensure data consistency and prevent issues with leader election, log replication, and cluster stability.
In an air-gapped environment, where external time sources are unavailable, maintaining an accurate and synchronized time becomes even more crucial. Without proper time synchronization, cluster nodes may experience authentication failures, scheduling issues, or even data corruption. To mitigate these risks, organizations should deploy a robust, internal NTP server that synchronizes time across all systems within the network.
Ensuring accurate and consistent time across the cluster is essential for reliability, security, and overall system integrity.
Troubleshooting
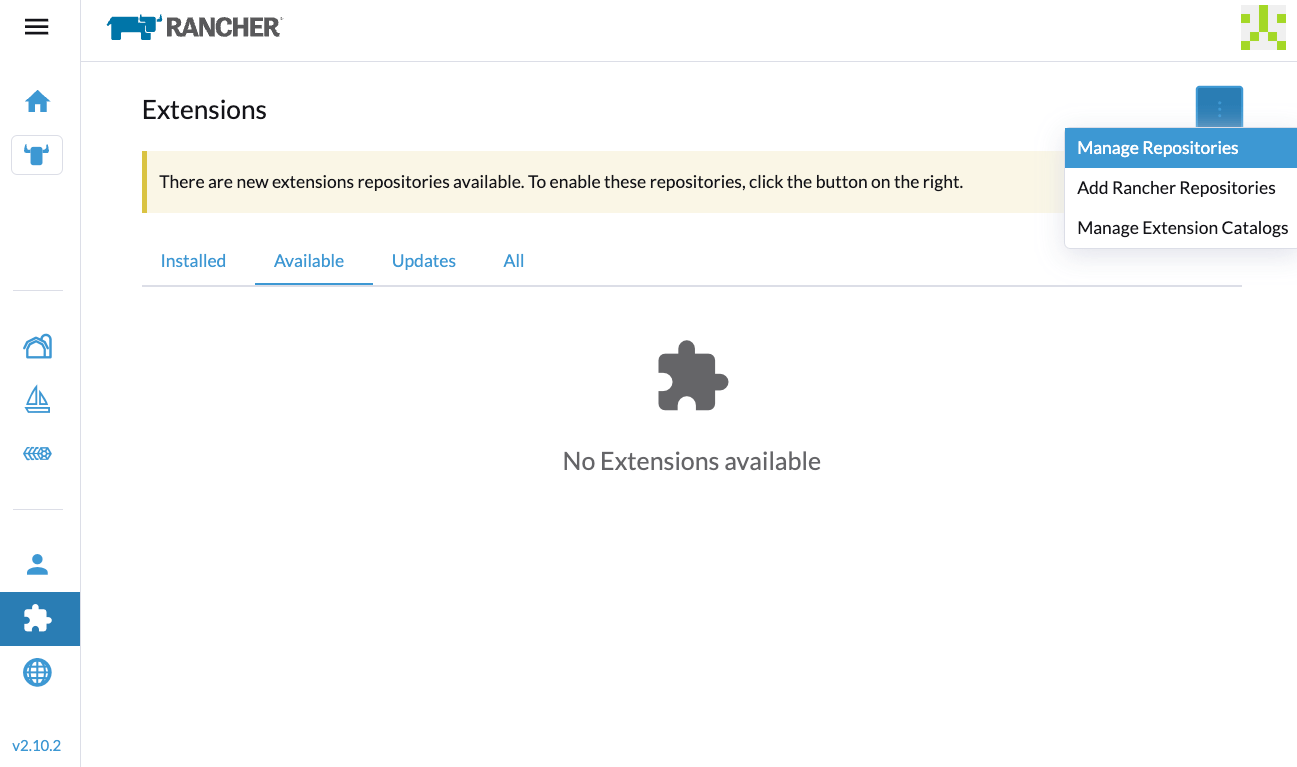
UI Extensions Do Not Appear
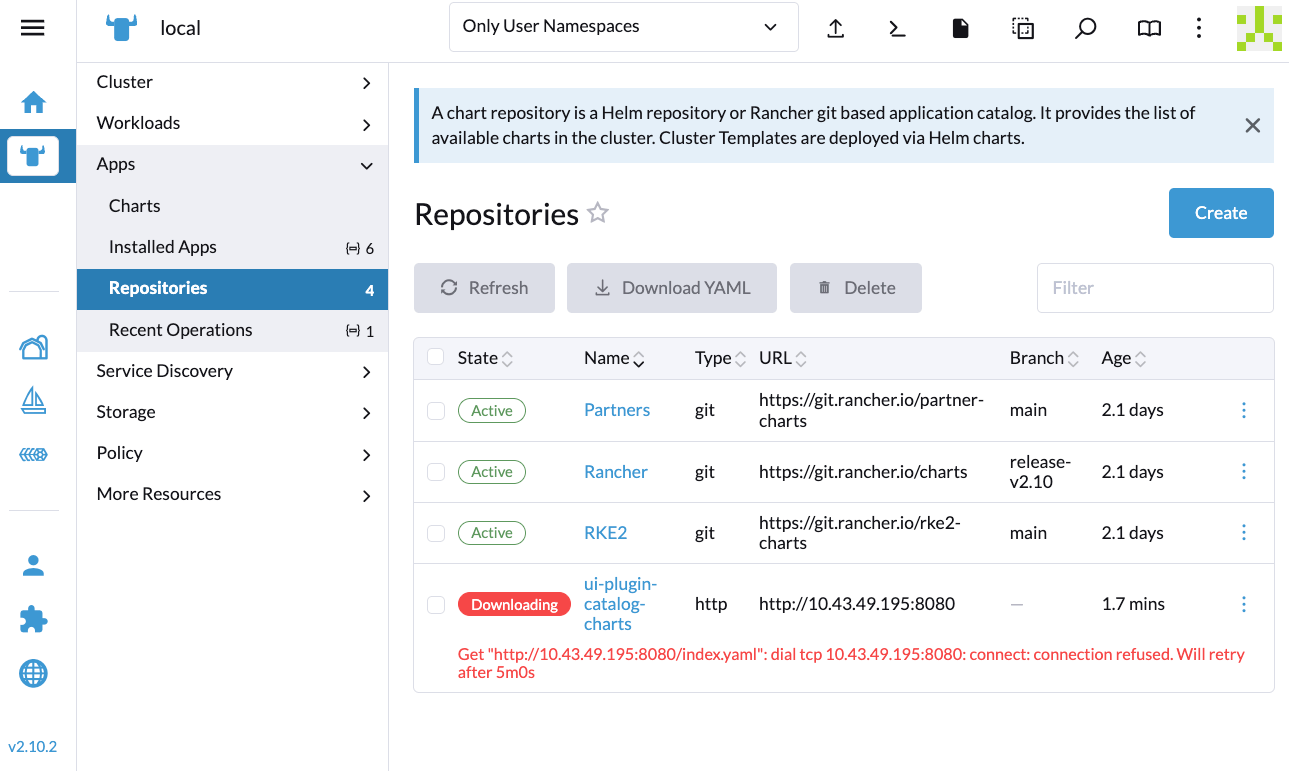
If the Extensions screen is empty, go to Repositories (⋮ > Manage Repositories) and then click Refresh.
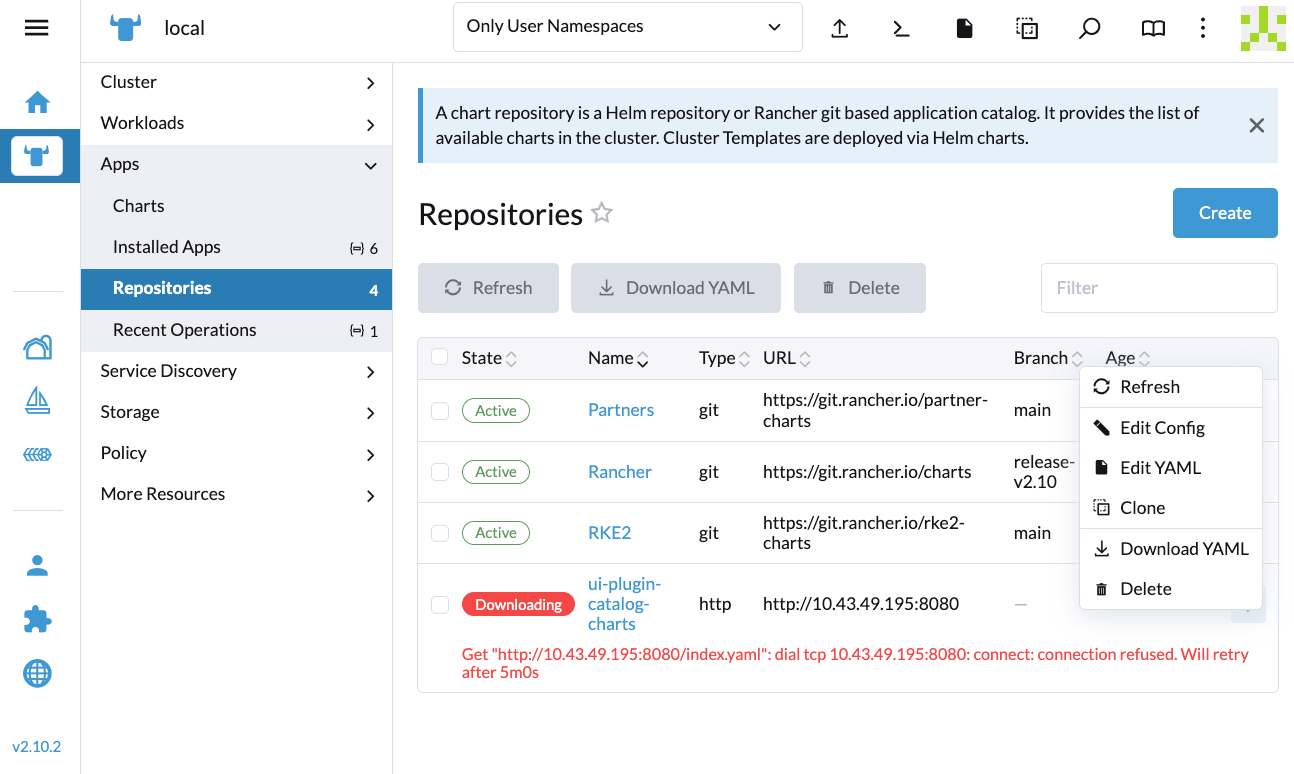
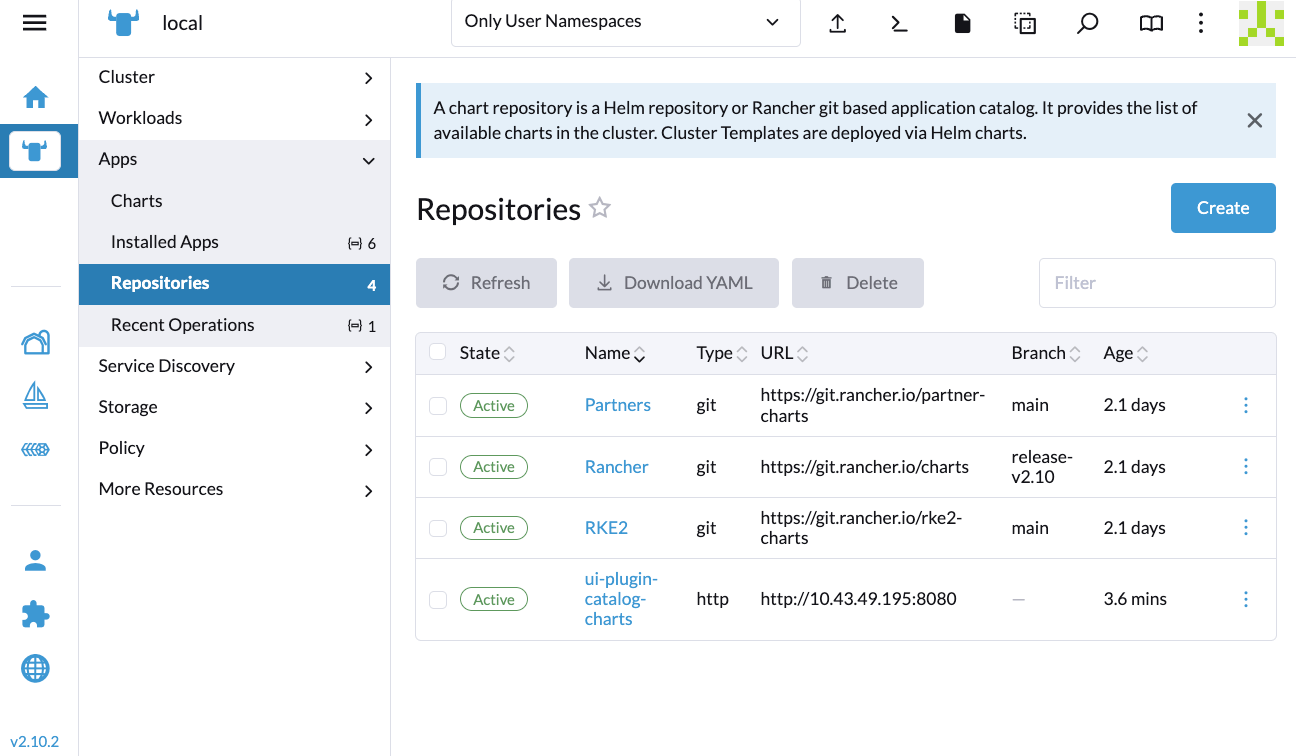
Installation Failed
If you encounter an error during installation, check the uiplugins resource.
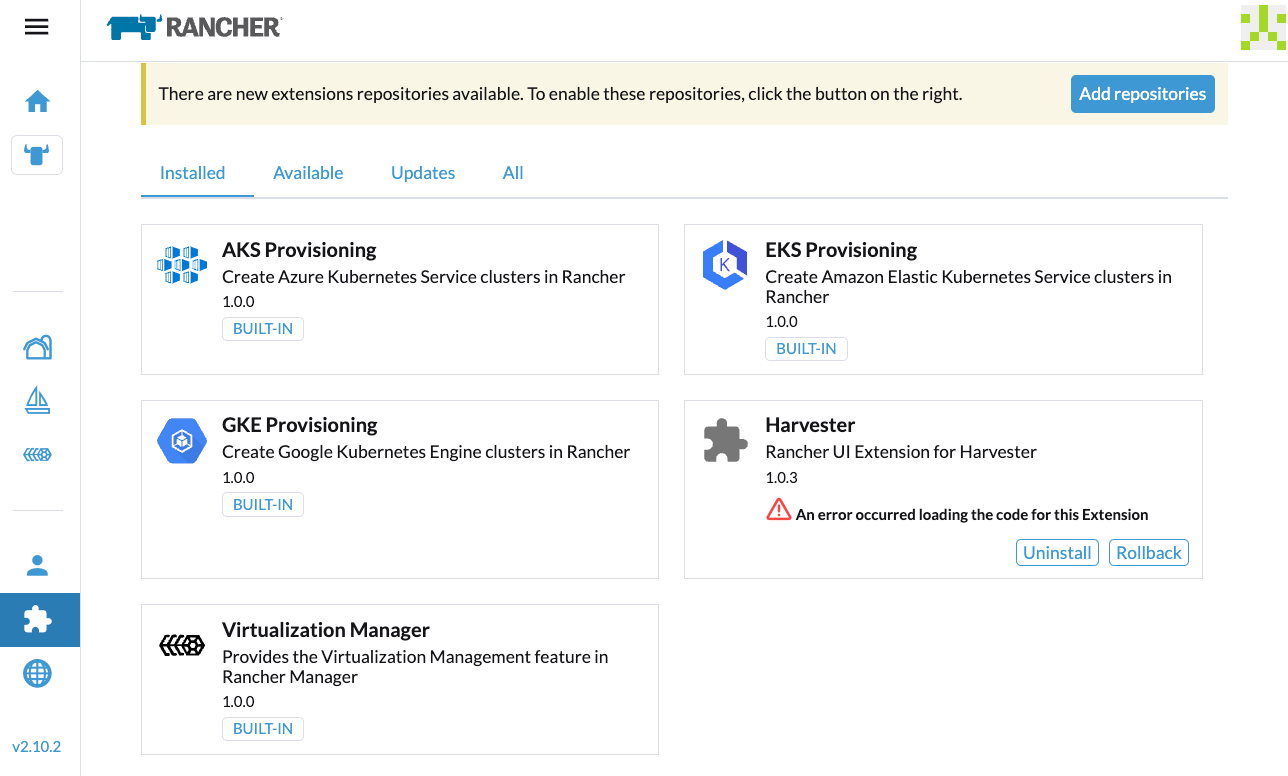
Example:
bash-4.4# k get uiplugins -A
NAMESPACE NAME PLUGIN NAME VERSION STATE
cattle-ui-plugin-system harvester harvester 1.0.3 pending
bash-4.4# k get uiplugins harvester --namespace cattle-ui-plugin-system -o yaml
apiVersion: catalog.cattle.io/v1
kind: UIPlugin
metadata:
# skip
name: harvester
namespace: cattle-ui-plugin-system
spec:
plugin:
endpoint: http://ui-plugin-catalog-svc.cattle-ui-plugin-system:8080/plugin/harvester-1.0.3
Ensure that svc.namespace is accessible from Rancher. If that endpoint is not accessible, you can directly use a cluster IP such as 10.43.33.58:8080/plugin/harvester-1.0.3.
Known issues
1. Missing rancher/rancher-agent:v2.9.2 image affects deployment in air-gapped environments. (Issue #7157)
Rancher v2.9.2, which is embedded in Harvester v1.4.0, introduced a new cronjob (rke2-machine-config-cleanup). This cronjob uses a container image (rancher/rancher-agent:v2.9.2) that is not included in the Harvester v1.4.0 ISO. To mitigate the issue, you can pull the image from the internet and then load it in the air-gapped environment.
# on a computer which can reach the internet and harvester cluster
docker pull rancher/rancher-agent:v2.9.2
docker save rancher/rancher-agent:v2.9.2 -o rancher-agent-v2.9.2.tar
# copy rancher-agent-v2.9.2.tar to the air-gapped environment
scp rancher-agent-v2.9.2.tar rancher@<harvester-node-ip>:/tmp
# ssh to the harvester node and load the image
ssh rancher@<harvester-node-ip>
sudo -i
docker load -i /tmp/rancher-agent-v2.9.2.tar