Creating an K3s Kubernetes Cluster
You can now provision K3s Kubernetes clusters on top of the Harvester cluster in Rancher v2.6.3+ using the built-in Harvester node driver.
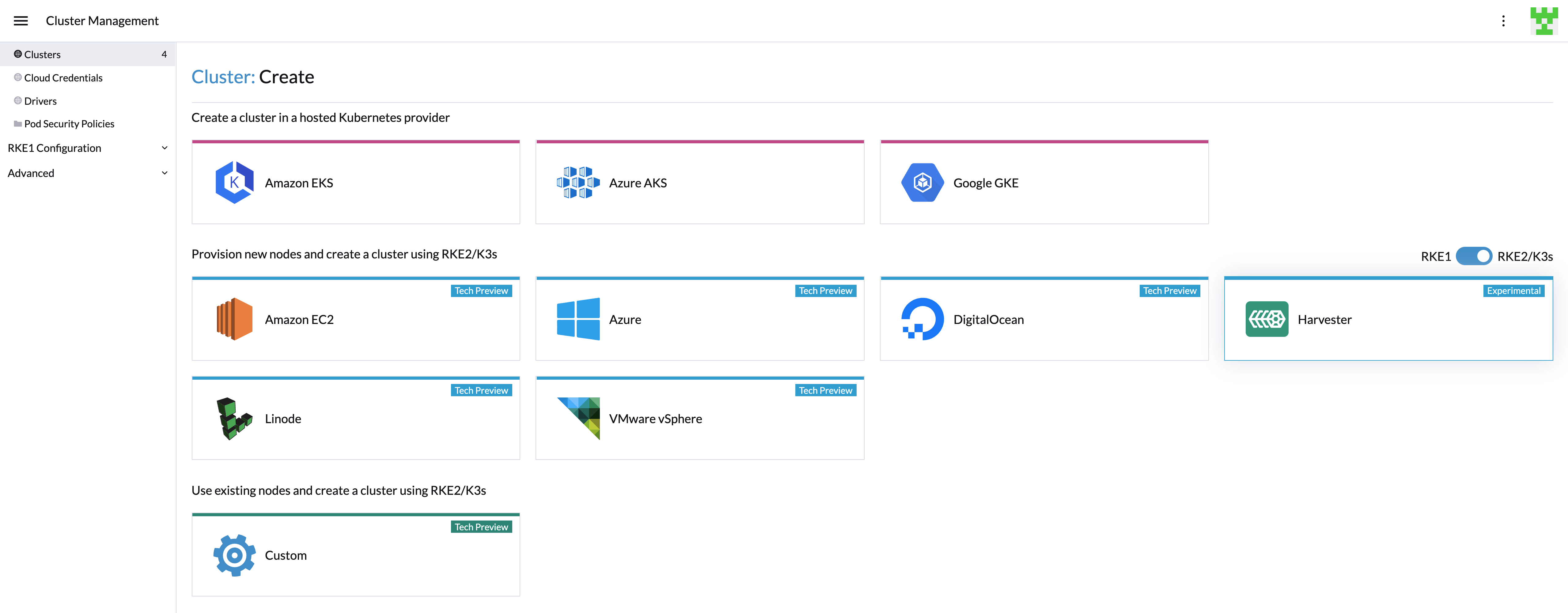
- Harvester K3s node driver is in tech preview.
- VLAN network is required for Harvester node driver.
Create Your Cloud Credentials
- Click ☰ > Cluster Management.
- Click Cloud Credentials.
- Click Create.
- Click Harvester.
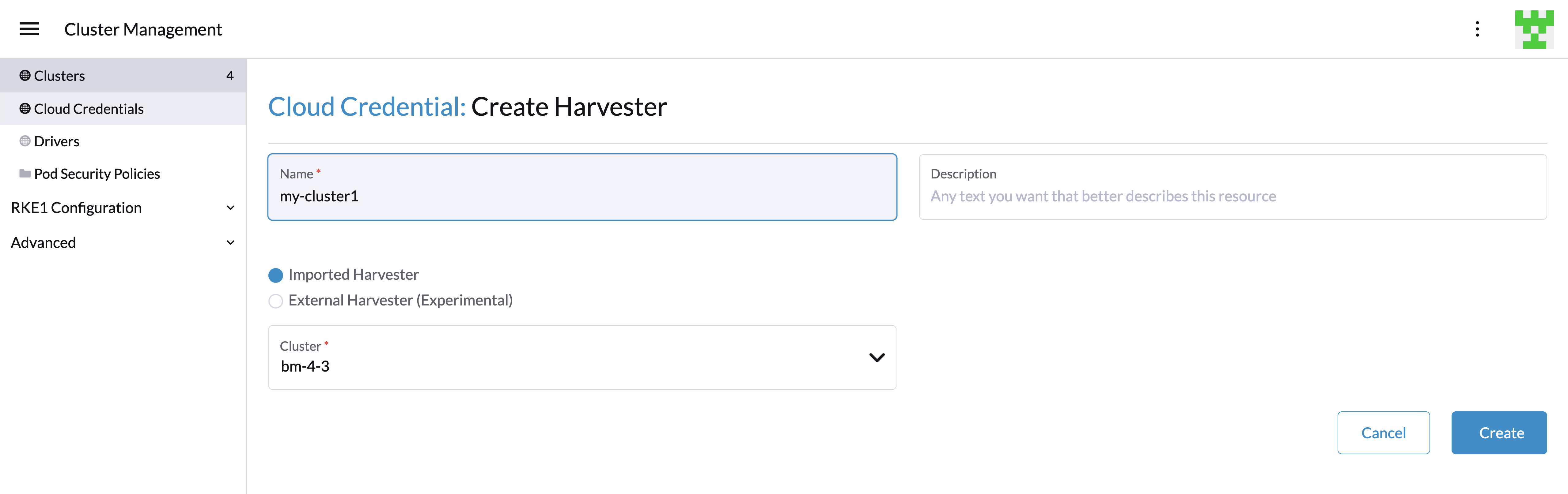
- Enter your cloud credential name
- Select "Imported Harvester" or "External Harvester".
- Click Create.
Create K3s Kubernetes Cluster
You can create a K3s Kubernetes cluster from the Cluster Management page via the K3s node driver.
- Select Clusters menu.
- Click Create button.
- Toggle Switch to RKE2/K3s.
- Select Harvester node driver.
- Select a Cloud Credential.
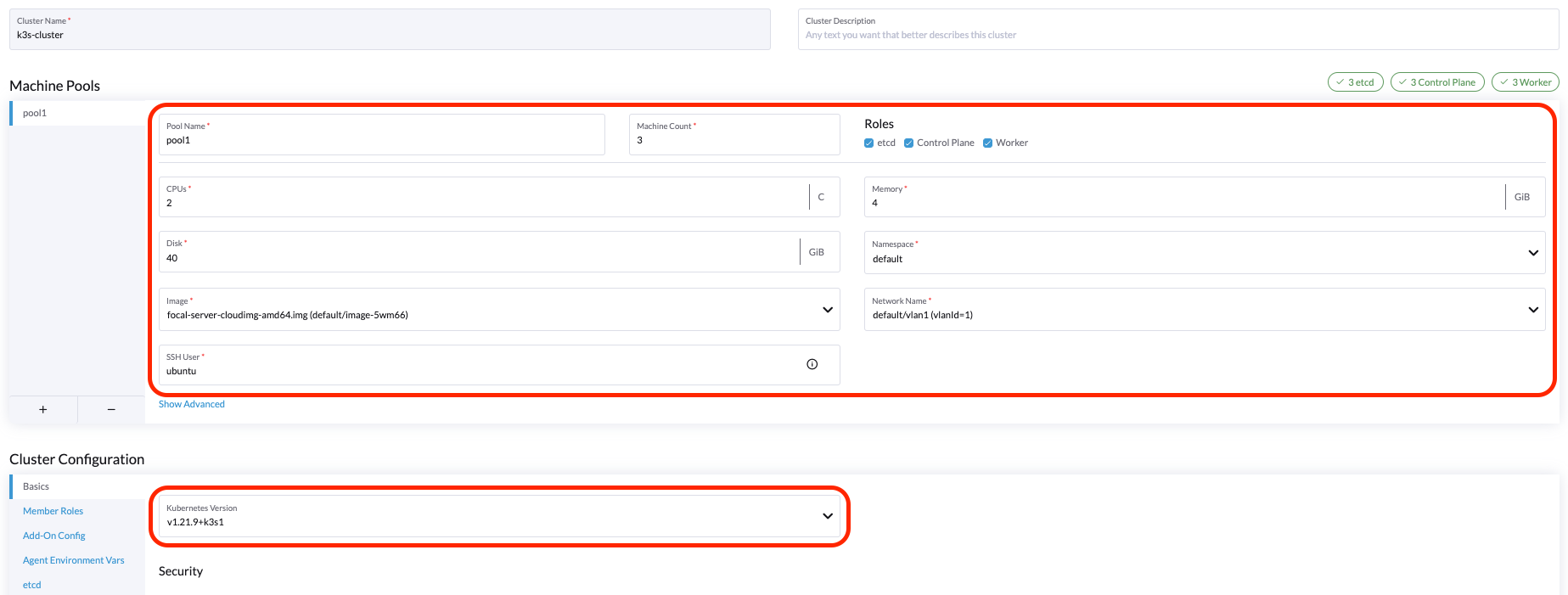
- Enter Cluster Name (required).
- Enter Namespace (required).
- Enter Image (required).
- Enter Network Name (required).
- Enter SSH User (required).
- Click Create.
Add Node Affinity
Available as of v1.0.3 + Rancher v2.6.7
The Harvester node driver now supports scheduling a group of machines to particular nodes through the node affinity rules. This provides high availability and better resource utilization.
Node affinity can be added to the machine pools during the cluster creation:
- Click the
Show Advancedbutton and click theAdd Node Selector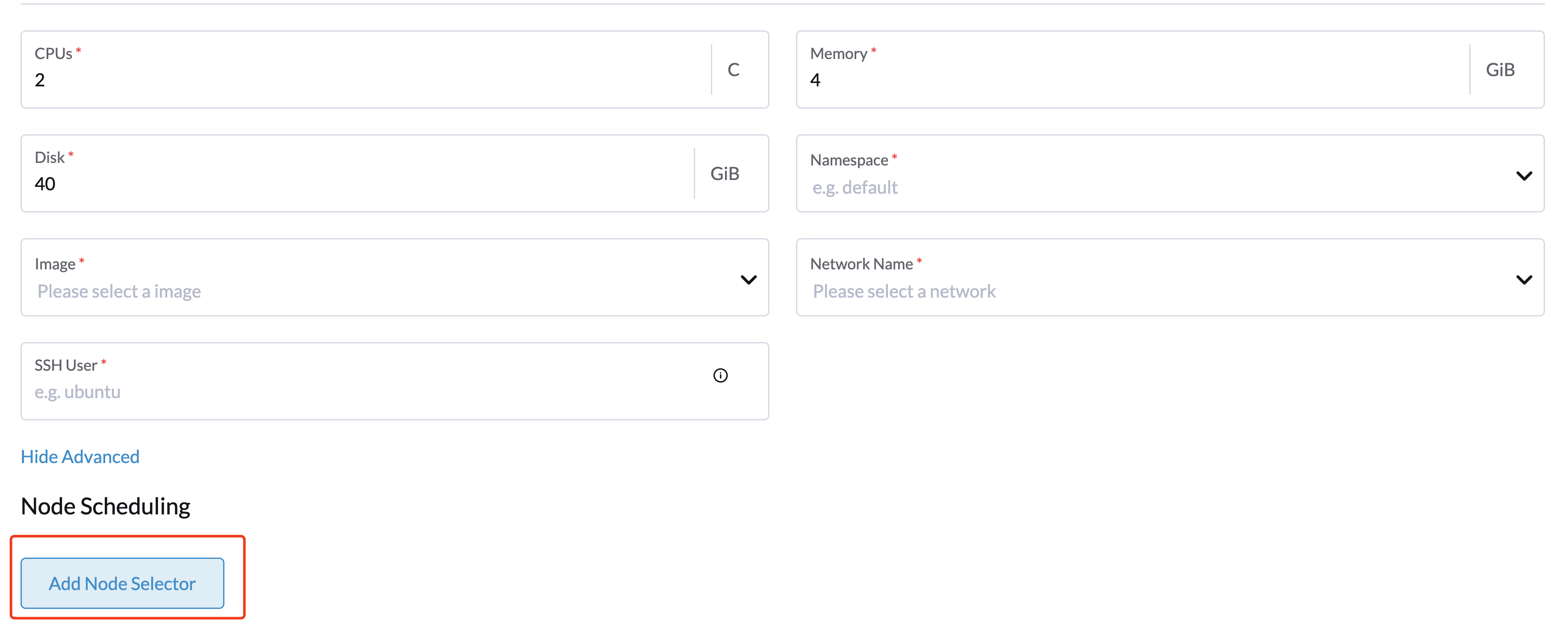
- Set priority to
Requiredif you wish the scheduler to schedule the machines only when the rules are met. - Click
Add Ruleto specify the node affinity rules, e.g., for the topology spread constraints use case, you can add theregionandzonelabels as follows:key: topology.kubernetes.io/region
operator: in list
values: us-east-1
---
key: topology.kubernetes.io/zone
operator: in list
values: us-east-1a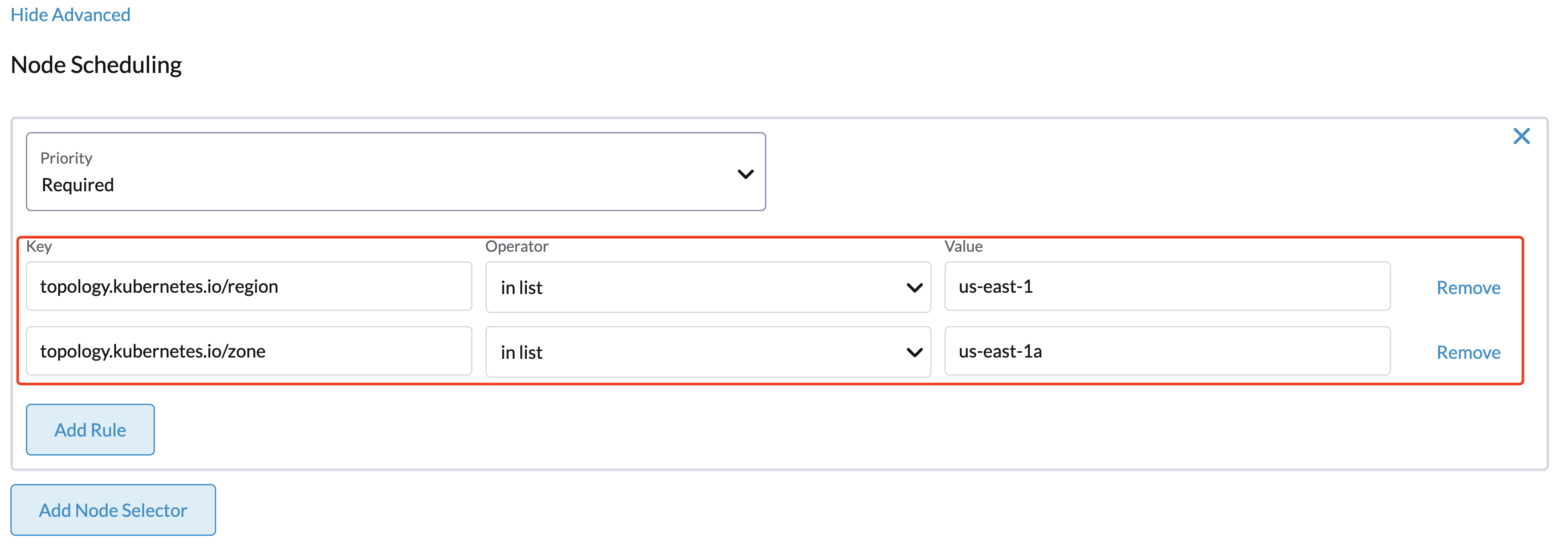
- Click
Createto save the node template. After the cluster is installed, you can check whether its machine nodes are scheduled according to the affinity rules.
Using Harvester K3s Node Driver in Air Gapped Environment
K3s provisioning relies on the qemu-guest-agent to get the IP of the virtual machine. However, it may not be feasible to install qemu-guest-agent in an air gapped environment.
You can address the installation constraints with the following options:
Option 1. Use a VM image with qemu-guest-agent installed.
Option 2. Configure the cloud init user data to enable the VMs to install qemu-guest-agent via an HTTP(S) proxy.
Example of user data in Harvester node template:
#cloud-config
apt:
http_proxy: http://192.168.0.1:3128
https_proxy: http://192.168.0.1:3128