Upload Images
Currently, there are three ways that are supported to create an image: uploading images via URL, uploading images via local files, and creating images via volumes.
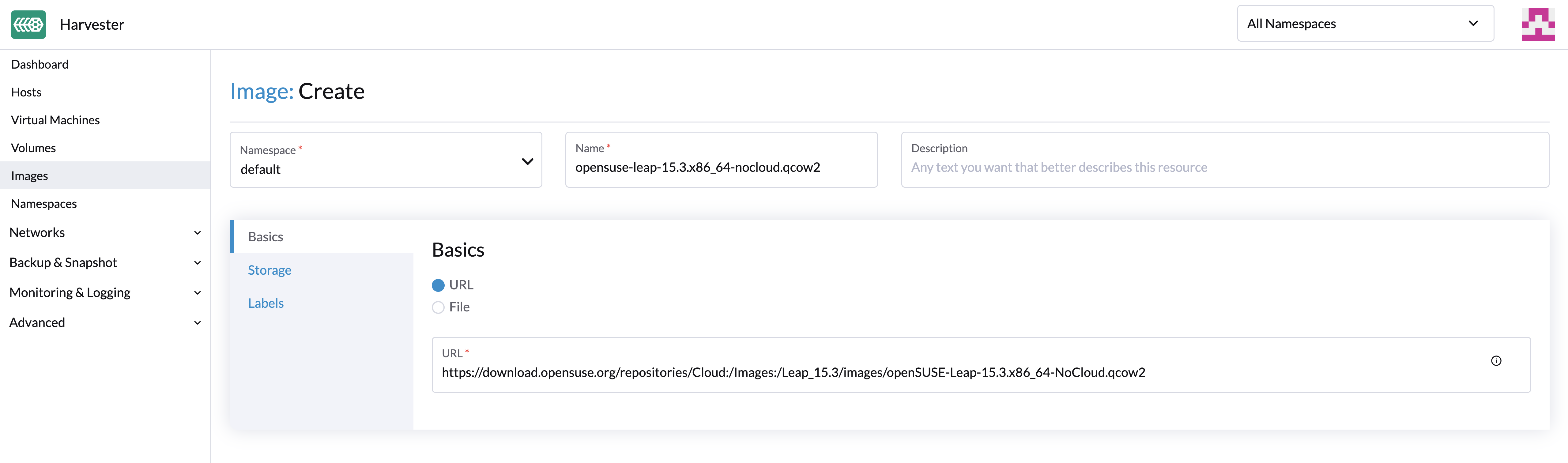
Upload Images via URL
To import virtual machine images in the Images page, enter a URL that can be accessed from the cluster. Description and labels are optional.
The image name will be auto-filled using the URL address's filename. You can customize the image name at any time.
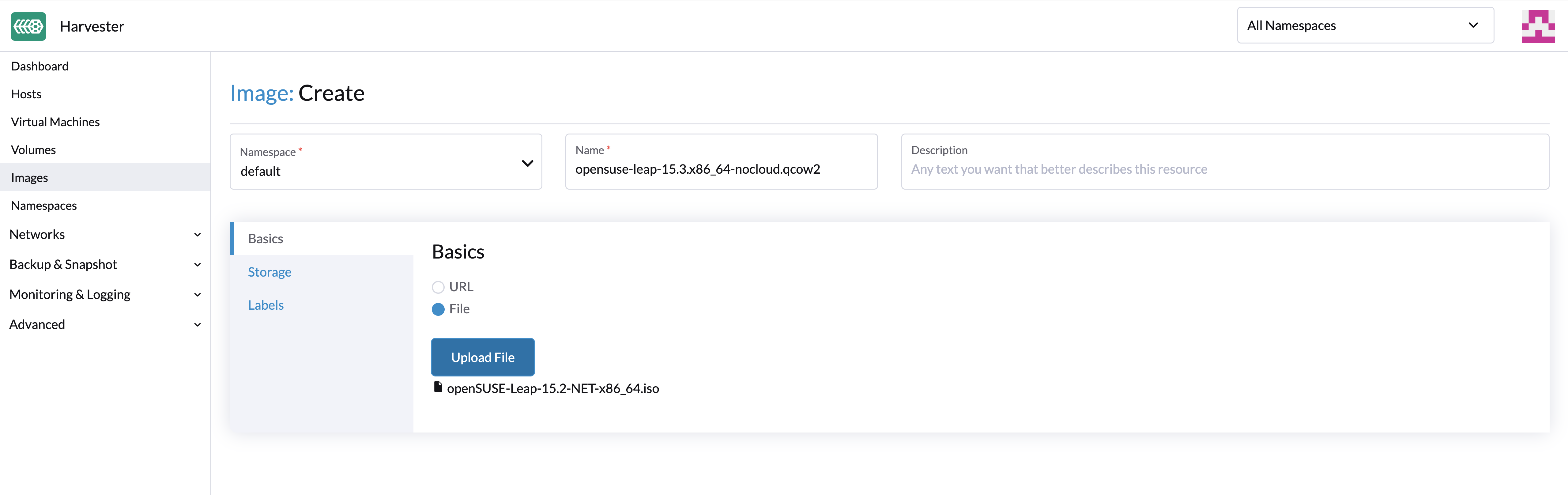
Upload Images via Local File
Currently, qcow2, raw, and ISO images are supported.
- Please do not refresh the page until the file upload is finished.
Create Images via Volumes
On the Volumes page, click Export Image. Enter the image name and select a StorageClass to create an image.
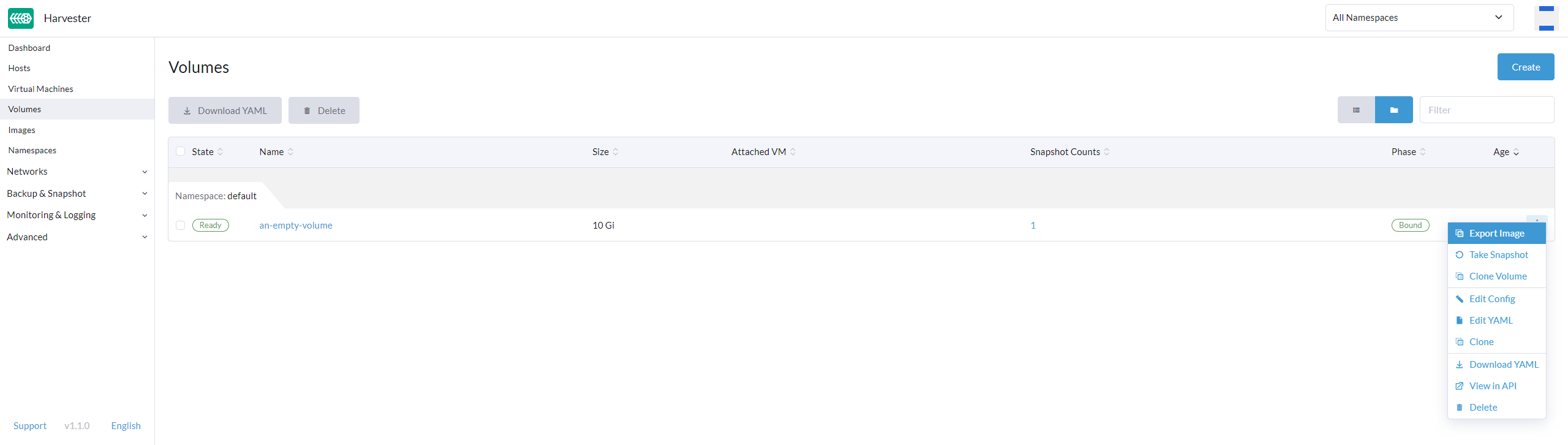
Image StorageClass
When creating an image, you can select a StorageClass and use its pre-defined parameters like replicas, node selectors and disk selectors .
The image will not use the StorageClass selected here directly. It's just a StorageClass template.
Instead, it will create a special StorageClass under the hood with a prefix name of longhorn-. This is automatically done by the Harvester backend, but it will inherit the parameters from the StorageClass you have selected.
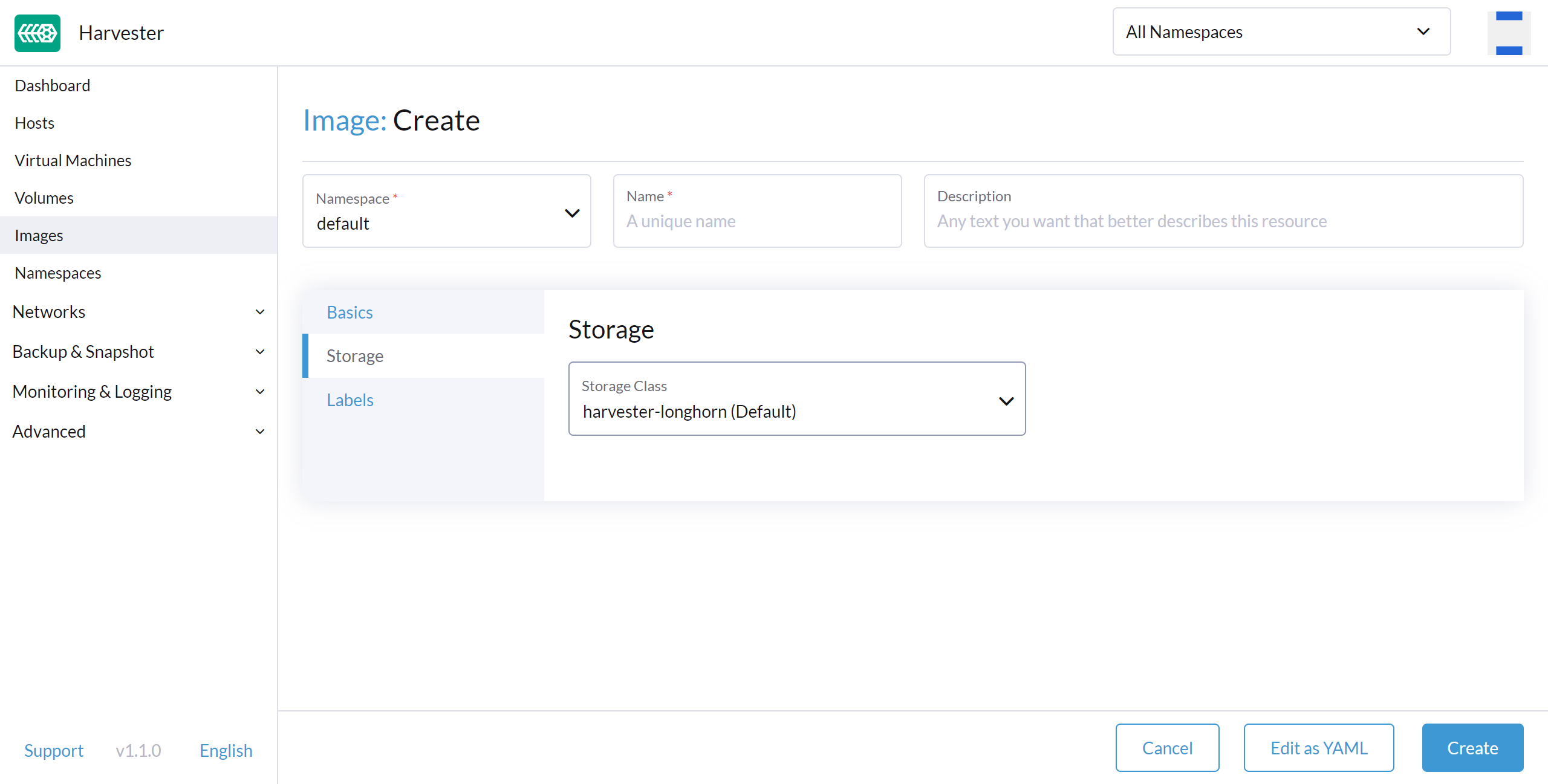
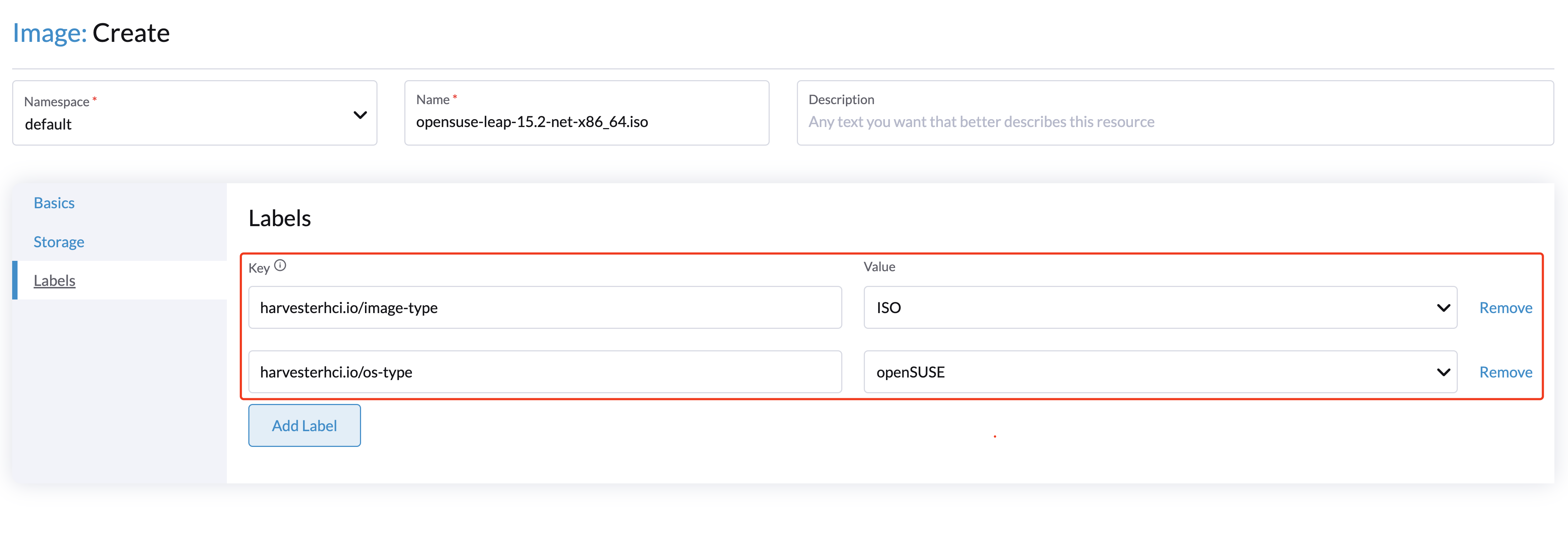
Image Labels
You can add labels to the image, which will help identify the OS type more accurately. Also, you can add any custom labels for filtering if needed.
If your image name or URL contains any valid information, the UI will automatically recognize the OS type and image category for you. If not, you can also manually specify those corresponding labels on the UI.
Known Issues
If you remove an image before the upload process is completed, the related Longhorn backing image may become stuck in the deletion state.
To determine if the issue has occurred, locate the backing image on the Dashboard screen of the Longhorn UI. If the deletion state has lasted for more than 5 minutes, perform the following steps:
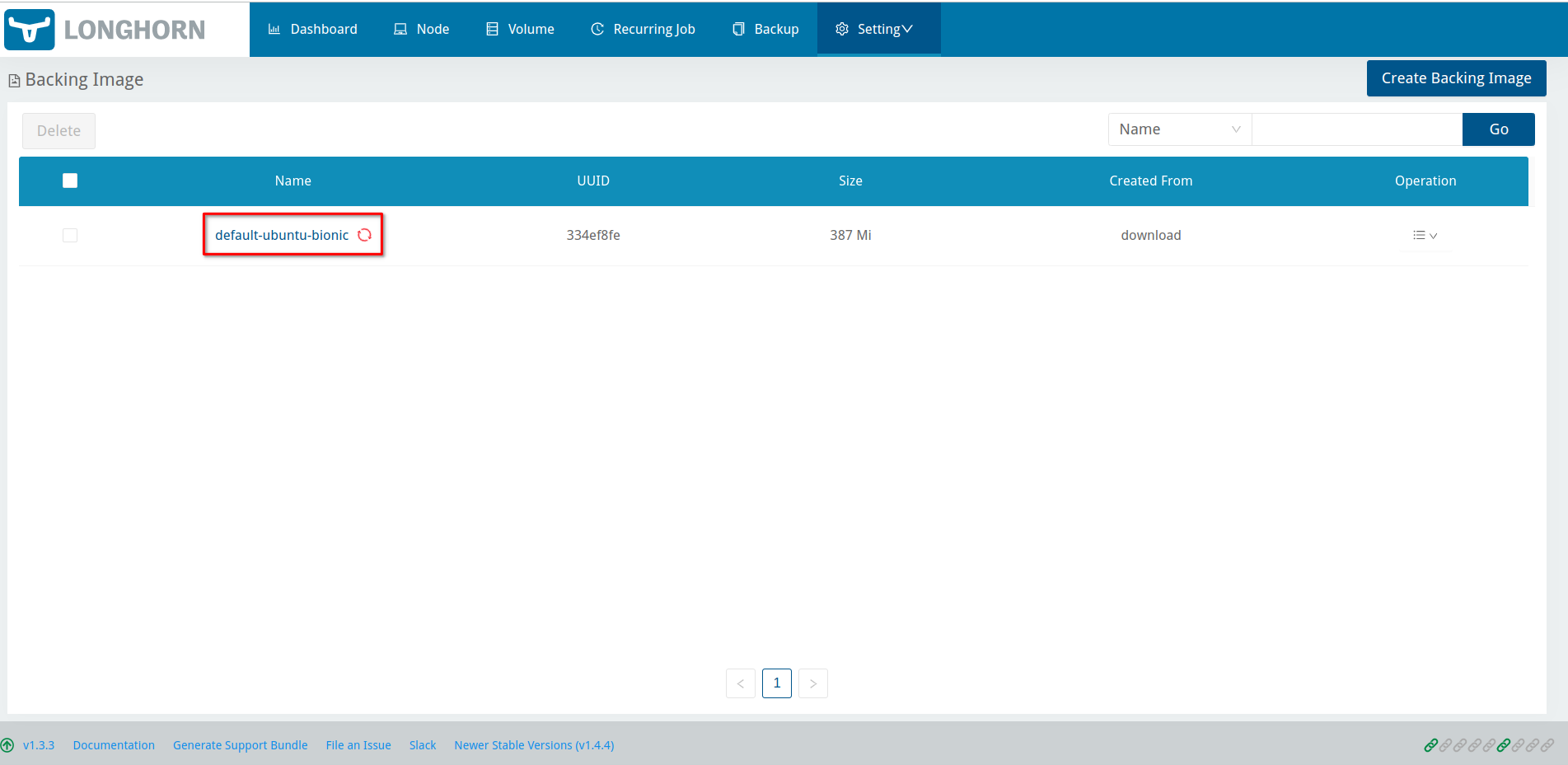
Verify that the deletion state has lasted for more than 5 minutes.
$ kubectl get backingimagedatasources.longhorn.io -A -o json | jq -r '.items[] | select(.metadata.deletionTimestamp != null) | .metadata.name + " deleted at: " + .metadata.deletionTimestamp 'Example:

Edit the affected backing image data source.
$ kubectl -n longhorn-system edit backingimagedatasources.longhorn.io <backingimagedatasource name>Example:
$ kubectl -n longhorn-system edit backingimagedatasources.longhorn.io default-ubuntu-bionicDelete the
finalizersmetadata of the affected backing image data source.Example:
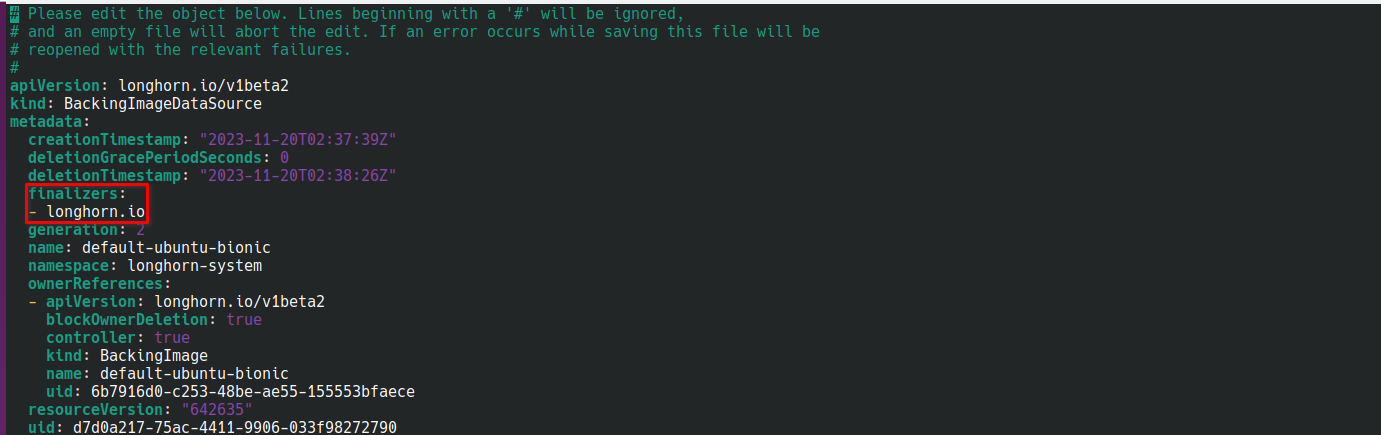 You must delete
You must delete finalizers:and- longhorn.io.The backing image should no longer be stuck in the deletion state.